As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
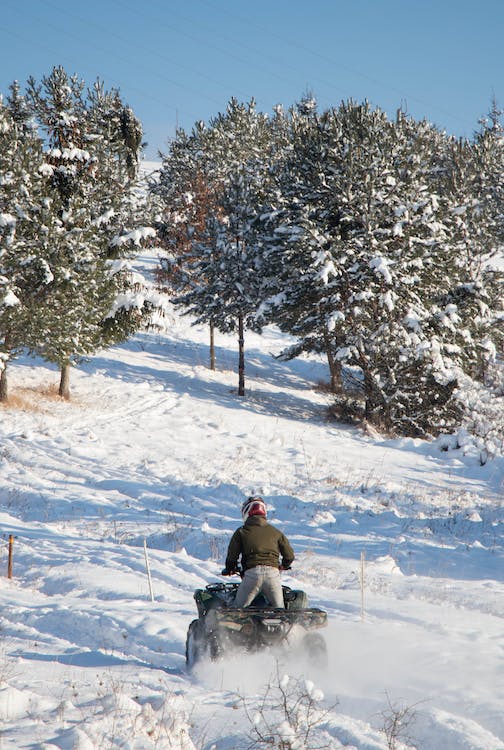
When it comes to off-road vehicles, understanding the differences between 2-stroke ATV performance and 4-stroke Side by Side torque can make all the difference in choosing the right ride.
2-stroke ATVs are often celebrated for their excellent power-to-weight ratio and swift acceleration.
Their design allows for a snappy and exhilarating ride, making them a favorite among those seeking high-speed thrills.

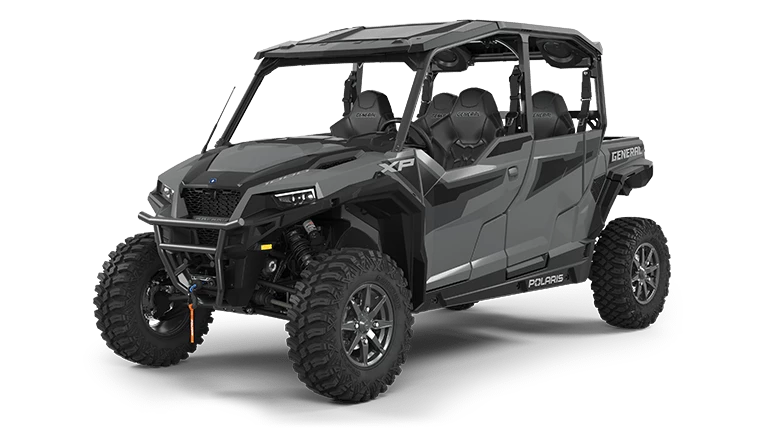
On the other hand, 4-stroke Side by Sides are known for their robust torque and consistent performance over varied terrains. They offer a smooth and reliable ride, capable of handling rugged paths with ease. The increased torque in these machines provides the power needed for steep climbs and heavy loads, attracting enthusiasts focused on endurance rather than speed alone.
Understanding Engine Types
When comparing 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines, key differences exist in power delivery and performance characteristics. These engines influence aspects like power stroke efficiency, rpm range, and torque production.
Distinctions Between 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engines
2-stroke engines complete a power cycle with two movements of the piston, generating power with each cycle. They often have simpler designs and fewer moving parts, leading to higher power-to-weight ratios.
This enables quicker acceleration and compact sizes, making them ideal for ATVs.
4-stroke engines have four movements: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. They are generally larger and heavier but operate more efficiently by using separate strokes for different processes. This leads to better fuel efficiency and cleaner emissions, which is suitable for side by sides.
Torque and Power Characteristics
Torque and power output differ notably between these engine types.
2-stroke engines generate a higher power output at higher rpm, providing rapid speed and acceleration. The power stroke occurs every second stroke, contributing to more explosive power delivery.
In contrast, 4-stroke engines excel in producing consistent torque. They achieve maximum torque at lower rpm, favoring off-road and towing capabilities. Despite their lower horsepower, they provide steady power and better traction, crucial for rugged terrains.
By examining engine displacement and compression ratio, one can further understand how these factors affect maximum torque and peak performance in each engine type.
Comparative Performance Metrics
When evaluating the performance metrics of 2-stroke ATVs compared to 4-stroke Side by Sides, key factors such as power dynamics and torque play crucial roles. Differences in engine design, weight, and drive systems contribute to their unique characteristics, impacting speed, acceleration, and overall performance.
2-Stroke ATV Power Dynamics
2-stroke ATVs are renowned for their lightweight design and high power output. The horsepower produced by these vehicles is often higher relative to their size, allowing for rapid acceleration and quickness.
They rely on a simpler engine mechanism, which results in a steeper torque curve. This means that 2-stroke engines can deliver power more abruptly, giving riders an explosive start.
The agility offered by 2-stroke ATVs makes them popular for off-road racing and environments where maneuverability is key. Their reduced weight further enhances their speed, allowing enthusiasts to navigate challenging terrains effectively. Despite these advantages, 2-stroke engines typically require more frequent maintenance to ensure peak performance.
4-Stroke Side by Side Torque Advantages
4-stroke Side by Sides excel in delivering consistent and robust torque, especially at lower RPMs. This offers a steadier power delivery than their 2-stroke counterparts.
The torque advantage is particularly beneficial in off-road settings, where climbing hills and tackling rough landscapes are common.
These vehicles tend to have a heavier build, offering greater stability and ground clearance, making them suitable for heavy-duty tasks. The drive systems employed in 4-stroke engines enhance control and power distribution. The improved efficiency and longer lifespan of 4-stroke engines are additional benefits, providing a reliable option for riders looking for durable performance.
Impact on Riding Experience
In comparing 2-stroke ATVs and 4-stroke Side by Sides, the riding experience varies significantly due to differences in power delivery and vehicle characteristics. Key factors include handling in diverse terrains and control dynamics influenced by engine type and vehicle design.
Handling and Control
2-stroke ATVs are known for their quick acceleration and lighter weight, which can translate to nimble handling. Riders often experience a more agile response in tight corners and racing circuits, giving an edge in situations demanding swift maneuvers.
In contrast, 4-stroke Side by Sides provide steadier control, thanks to their built-in torque capabilities. The heavier build offers more stability, allowing drivers to navigate rugged terrains with ease. The power and torque balance ensures less wheel spin, making these vehicles suitable for controlled driving scenarios, like sand and mud.
Side by Sides also showcase superior traction when fitted with specialized tires, such as paddle tires designed for sandy locales. This is particularly noticeable in environments like sand dunes or on drag racing tracks, where traction is key to performance.
Terrain and Usage Considerations
When considering terrain, 2-stroke ATVs excel in environments where rapid acceleration is crucial, such as racing circuits or drag racing events. Their capability to rev quickly offers an advantage, but handling can become challenging on slick or uneven surfaces, where traction is at a premium.
4-stroke Side by Sides, owing to their engine torque and weight, are adept at traversing varied terrains, including sandy or muddy areas. Their robust build allows for more substantial payloads, benefitting utility and recreational users who desire reliable travel over unpredictable landscapes.
Snow-covered terrains, reminiscent of those favored in the snowmobile market, also benefit from the torque of Side by Sides. The vehicles’ design lends itself to better control in low-traction conditions, providing a balanced mix of power and stability.
Technical Specifications Analysis
In analyzing the technical specifications of 2-stroke ATVs and 4-stroke Side by Sides, it is crucial to compare their engine systems and transmission setups. These factors significantly influence performance characteristics, engine efficiency, and operation on different terrains.
Engine and Transmission Systems
2-stroke engines are favored for their simplicity and high power-to-weight ratio. They complete a power cycle in two movements of the piston: a compression and a power stroke. This results in more immediate power delivery, which is ideal for off-road racing. Typically, their design incorporates a single cylinder with a carburetor to mix fuel and air.
4-stroke engines, with their complex mechanisms, deliver power through a four-step cycle: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. These engines often provide more torque at lower RPMs. 4-stroke models might include reverse gear capabilities, improving maneuverability in tight spaces. Such engines favor efficiency and durability in varied conditions.
Comparing Displacement and Compression
Engine displacement is a critical factor influencing power output. 2-stroke engines frequently have smaller displacements but higher power-to-displacement ratios. This means they can produce significant power from a compact engine, making them lightweight yet powerful for certain applications.
4-stroke engines often have larger displacements with a focus on torque and endurance. Their compression ratio is typically higher, which enhances fuel efficiency. This characteristic allows for smoother power delivery and better fuel economy.
The choice between these engines should consider the operating environment and performance needs. It’s important to weigh the power advantages of the 2-stroke against the torque and efficiency offered by the 4-stroke engine types.
Maintenance and Reliability
Maintaining ATVs and Side by Sides involves understanding the distinct needs of 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. Each engine type has unique maintenance routines that impact their long-term reliability and performance.
Routine Maintenance Needs
2-stroke engines require frequent maintenance due to their simplistic design. Regular tasks include checking the oil-fuel mixture, cleaning exhaust ports, and inspecting spark plugs.
Since 2-strokes typically lack an oil reservoir, the oil must be mixed with fuel, demanding attention to fuel mixture ratios for optimal performance.
In comparison, 4-stroke engines, while more complex, require regular oil changes and valve adjustments. This complexity often results in less frequent, though potentially more involved, maintenance sessions.
Both engine types require regular air filter cleaning and lubrication checks to ensure they remain in peak condition.
Long-Term Reliability Factors
Long-term reliability varies between engine types due to their construction and operational demands.
2-stroke engines tend to wear faster because they run at higher RPMs and depend on a fuel-oil mix, affecting their lifespan. Despite this, they offer simplicity in repairs, often at a lower cost.
4-stroke engines provide more robust durability due to their design, offering generally longer lifespans. They frequently conform better to EPA emissions standards, often featuring better fuel economy.
However, their complexity may result in more expensive repairs, though they usually come with better warranty options. Users should consider these aspects alongside routine care to sustain reliability.
Brand Comparisons

When considering power characteristics in ATVs and Side by Sides, Yamaha and Honda have a long-standing rivalry defined by innovation and reliability. Polaris and Arctic Cat are known for their unique performance elements catered to enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Yamaha vs. Honda: A Historical Perspective
Yamaha and Honda stand as icons in the ATV world, each with a rich history of innovation and excellence. Yamaha is celebrated for its 2-stroke models, offering a blend of lightweight design and responsive power delivery, making them ideal for a spirited ride. The Banshee is a notable model with a dedicated following.
Honda, known for its 4-stroke engineering, is lauded for durability and consistent torque output. The company often incorporates technology from its motorcycles, ensuring a balance between performance and fuel efficiency. The Honda TRX450R is a prime example, unmatched for its reliability in competitive settings. This historical rivalry has pushed both brands to focus on continual improvements and technological advancements.
Polaris and Arctic Cat Performance Review
Polaris impresses with robust 4-stroke Side by Sides, like the RZR series, applauded for off-road capability and torque. It focuses on innovation, designing vehicles that handle extreme terrains while maintaining comfort.
Arctic Cat, meanwhile, delivers exhilarating 2-stroke ATV performance with models like the Wildcat series. Featuring agile handling and impressive acceleration, they are tailored for speed enthusiasts. This brand leverages bold designs and advanced engineering. Both have set benchmarks in the industry, often compared on platforms like Can-Am for versatility and Bombardier for their bold advancements. These brands push the boundaries of what off-road machines can achieve.
Environmental and Regulatory Impacts

The environmental and regulatory impacts of ATVs and Side by Sides can be significant. Emissions standards, fuel types, and advancements in clean technology play pivotal roles in shaping how these vehicles affect their surroundings.
Emissions Standards and Fuel Types
Emissions standards, particularly in the U.S. under the EPA, set strict limits on pollutants from engines. 2-stroke engines, used in some ATVs, are less efficient in burning fuel, often leading to higher emissions when compared to 4-stroke engines. These pollutants contribute to air pollution and environmental degradation.
The fuel types used further affect emissions. XD100 and other advanced fuels aim to reduce the carbon footprint. Unlike traditional gasoline, these are formulated to burn cleaner, directly impacting emissions. These fuels can enhance the efficiency of the 2-stroke engines but are crucial for improving the 4-stroke engines’ fuel mileage.
Advancements in Clean Technology
Advancements in clean technology target emissions control. Modern 4-stroke engines typically incorporate technologies like electronic fuel injection and advanced combustion techniques to optimize fuel usage and minimize emissions.
2-stroke engines are also benefiting from innovations, although they are inherently less efficient. Manufacturers strive for better emissions control and fuel efficiency, embracing catalytic converters and other technologies. These innovations are essential for meeting regulatory demands and ensuring that both engine types maintain compliance and improve their environmental footprint.
Advancements in Engine Technology

Recent innovations in engine technology have focused on enhancing efficiency and performance. These advancements include refined porting and exhaust systems, and more efficient fuel injection systems resulting in improved power delivery and torque.
Porting, Exhaust, and Fuel Systems
Modern two-stroke and four-stroke engines utilize advanced porting and exhaust designs to maximize airflow and efficiency. Port timing has been optimized in engines like the Evinrude E-TEC, enhancing combustion efficiency and power output. High-Pressure Direct Injection (HPDI) systems, such as Pro XS models, improve fuel delivery precision.
The integration of Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) systems ensures optimal air-fuel mixture, improving performance and reducing emissions. These components work in synergy to deliver enhanced dyno results, showcasing notable improvements in both power and efficiency.
The Shift Towards Lightweight Design
New materials and design strategies prioritize weight reduction without sacrificing durability. Engines like the Rotax series incorporate lightweight aluminum and advanced composites. These materials contribute to the agility and responsiveness of vehicles, especially the two-stroke ATVs.
Such innovations not only reduce engine weight but also improve the power-to-weight ratio, enhancing torque and acceleration. The focus on lightweight design aligns with engine work optimizations, ensuring modern engines are more powerful and efficient than ever before.
Aftermarket and Performance Tuning

Enhancing performance in 2-stroke ATVs and 4-stroke Side by Sides involves tuning for specific conditions and employing aftermarket modifications. These adjustments aim at optimizing power output, peak torque, and transmission efficiency to meet varied racing demands.
Tuning for Race Conditions
Racers often focus on adjusting the engine and drivetrain for race-specific performance. Porting and polishing the engine can significantly boost airflow, enhancing both horsepower and torque. Transmission tuning is crucial in achieving the desired power delivery, especially for different track types.
Using a dynamometer, or dyno, enables precise measurement of power output. This information is crucial when making adjustments to the fuel injection or carburetor for optimal air-fuel ratios. Tuning the suspension and brakes further ensures that the vehicle remains competitive under varying race conditions.
Aftermarket Upgrades and Modifications
To gain a competitive edge, drivers invest in aftermarket upgrades such as performance exhausts and high-performance air filters. Both of these contribute to increased horsepower and torque.
Engine upgrades like bigger pistons and stroker kits are popular for enhancing overall engine displacement and power.
The addition of aftermarket ECU units allows more precise control over engine parameters, facilitating better performance tuning.
For 2-stroke ATVs, specialized reed valves provide improved intake efficiency, while throttle body upgrades are popular in Side by Sides for enhanced power delivery.
These modifications push vehicles to achieve their peak torque and horsepower potential on the track.