As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
Navigating trails with All-Terrain Vehicles (ATVs) or Side by Sides offers thrilling adventures, yet the dynamics of group riding can differ significantly between these vehicles. Each requires specific guidelines to ensure both safety and enjoyment.
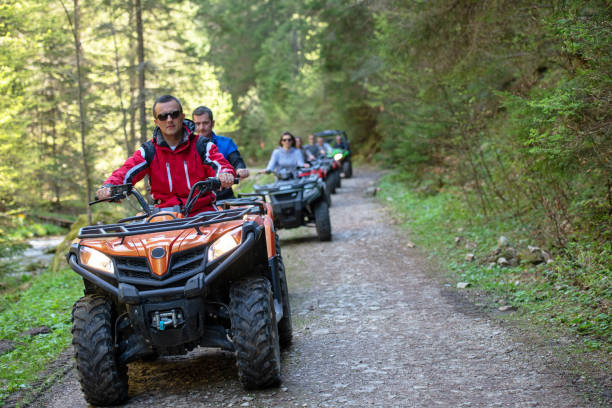
In group rides, ATVs often focus on maintaining a staggered formation, which helps prevent accidents and allows for quick maneuvers.

Side by Side convoys, on the other hand, follow different practices due to their distinct build and handling characteristics. These larger vehicles benefit from a more linear formation that accommodates their size and enhances communication among drivers. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone looking to optimize their group-riding experience.
Discovering the nuances between these approaches can greatly enhance the enjoyment of outdoor excursions. By adhering to the best practices suited for each vehicle type, group outings can be made safer and more pleasurable for everyone involved.
Conceptual Overview
Group riding with ATVs and Side by Sides involves unique practices for ensuring safety and cohesion. Each style of riding addresses different needs and comes with its own set of rules and guidelines to follow, particularly in operations involving navigation and transportation.
Definition of Group Riding
Group riding refers to the practice where multiple vehicles travel together as a cohesive unit. This approach is significantly influenced by the need for coordinated movement and communication.
Riders must align in close formation for safety and efficiency. The goal is to maintain a flexible structure that can adapt to terrain and other factors. Proper training ensures seamless synchronization, whether for recreational outings or military transportation.
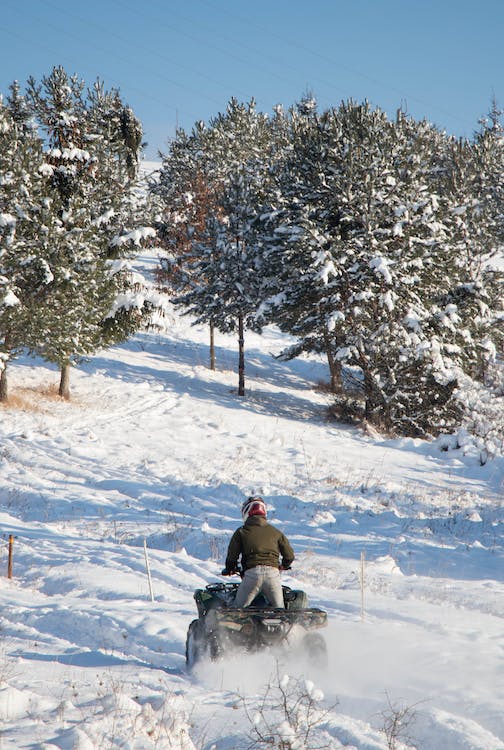
ATV Formation Fundamentals
ATV formations often require single-file lines where each rider maintains a safe distance. This setup is vital for navigating trails, both on rough and smooth terrain.
Communication through hand signals is crucial to convey changes in direction or speed. It’s essential that riders are trained to handle various situations, including emergency stops and obstacles. These practices support operations needing precision and are often used in recreational, military, and tactical settings.
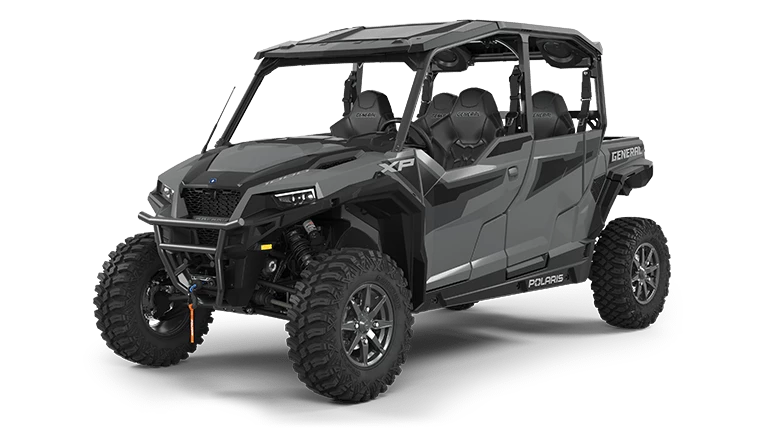
Side by Side Convoy Basics
Side by Side convoys emphasize a broader vehicle, allowing for more stable navigation through varying terrains. These vehicles can carry more passengers, making them ideal for troop transportation.
The convoy setup typically involves staggered formations to maximize visibility and maneuverability. Clear communication paths are necessary, whether through radio or visuals. Training focuses on handling difficult routes while maintaining convoy integrity, essential for both civilian adventures and strategic military operations.
Pre-Ride Preparation
Before embarking on any group ride, careful attention to personnel, equipment, weather, and route planning ensures a safe and efficient journey. These elements are critical for both ATV formations and Side by Side convoys, enhancing readiness and minimizing disruptions.
Assessing Personnel and Equipment
Personnel selection and equipment inspection are vital for a successful ride. Riders should be physically fit and adequately trained, particularly in military settings like the National Guard or U.S. Army. Helmets and protective gear must meet safety standards.
ATVs and Side by Side vehicles should be checked for mechanical issues. Regular maintenance, such as inspecting brakes, tires, and engines, prevents accidents. In convoy settings, ensuring that any necessary ordnance is securely stored is essential for safety.
Weather Considerations
Checking weather conditions is crucial for planning a group ride. Weather can affect both safety and performance.
Extreme heat or cold can be dangerous for riders and may impact the function of the vehicles. Rain or snow can also alter terrain conditions, making navigation more challenging.
The military, like the National Guard, often uses specialized weather forecasts to anticipate adverse conditions. Riders should remain adaptable, preparing for sudden changes in temperature or precipitation by carrying the appropriate gear.
Route Planning and Navigation
Careful route planning and navigation are necessary to avoid hazards and ensure a smooth ride. Maps and GPS systems assist in determining the safest paths, especially in unfamiliar areas.
Group leaders should should account for terrain difficulties, rest stops, and vehicle fuel ranges when planning routes.
Convoy practices differ slightly; maintaining communication between vehicles is key to avoiding separation. The use of military-grade navigation tools can enhance coordination in both ATV and Side by Side groups. Marking key waypoints on physical or digital maps aids in maintaining direction and facilitates quick responses to changes or emergencies.
Formation and Convoy Basics
Effective formation and convoy management are critical for both ATV group riding and Side by Side convoys. Understanding key formation guidelines for ATVs and best practices for Side by Side convoys ensures safety and efficiency in any riding mission or deployment.
Key Formation Guidelines for ATVs
ATV riders must maintain a strategic formation to ensure safety and coordination. Staggered formations allow for efficient visibility and reaction time. Riders should keep a safe distance to prevent collisions, especially when maneuvering complex terrains.
In missions involving possible ambush scenarios, maintaining a tight but flexible formation is crucial. In national defense operations, ATV groups may play a supporting role, requiring precision deployment and swift airborne adaptation. Each rider should position with clear lines for communication, allowing rapid responses to changing conditions.
Best Practices for Side by Side Convoys
Side by Side convoys benefit from structured convoy practices, intended to optimize space and communication. Vehicles should maintain even spacing, reducing risks in emergency stops. Radio communication is essential for informing drivers about changes in pace or direction.
Convoys on national defense missions may integrate roles such as lead vehicles and tail gunners to protect against threats. Ambush scenarios require readiness to alter convoy structure quickly. Each vehicle plays a distinct role, whether for covering deployment on rough terrain or facilitating swift airborne communication. Adhering to these practices enhances convoy effectiveness in varied conditions.
Operational Procedures

ATV formation guidelines and Side by Side convoy practices are critical when considering operational effectiveness and safety. This section covers essential procedures including communication, emergency response, and security measures.
Communication Protocols
Effective communication is crucial for ensuring smooth operations. Teams often utilize two-way radios or intercom systems, adopting clear and concise language.
It’s advised to assign specific call signs to each rider or vehicle. This minimizes misunderstandings and enhances operational efficiency.
Standard phrases should include directions, status updates, and alerts. Communication protocols often inspired by military structures ensure seamless information flow. All members must confirm receipt of critical messages, and maintain consistent checks throughout the ride.
Responding to Emergencies
In any convoy, preparation for potential emergencies is essential. Each team member should be familiar with basic first aid and emergency protocols specific to their equipment and terrain. Pre-ride briefings should cover emergency roles, such as designating a lead medic.
Having a well-equipped first aid kit and knowledge of nearby medical facilities or military bases for more severe injuries is vital. Team leaders must establish a clear plan for contact with local emergency services and ensure all members know how to execute it promptly.
Convoy Security Measures
Security in convoys involves vigilance and preparedness against both environmental and human threats. Maintaining a secure perimeter is a priority, often achieved by spacing vehicles strategically. Riders should adopt combat air patrol techniques for situational awareness.
Vehicles at the front and rear typically take on enhanced protective roles, mirroring military convoy strategies. Checkpoints may be established for prolonged rides to maintain security and check on each vehicle’s status. Convoys benefit from clearly defined drill practices, ensuring all members can respond swiftly to security threats.
Equipment and Machinery

Understanding the essential aspects of equipment selection, maintenance, and safety is crucial in group riding.
Selecting Suitable ATVs and Side by Sides
When selecting equipment for group riding, choosing the right ATV or Side by Side is key to performance and safety. ATVs offer greater maneuverability and are often preferred for solo rides on rough terrains. Side by Sides carry multiple passengers and provide more stability on various surfaces.
Considerations include engine power, suspension, and seating capacity. The military and NATO may use these vehicles for different terrains, tailoring their selection to mission requirements. For instance, the Quartermaster Corps may prioritize cargo capacity for logistical operations. In recreational settings, ensuring compatibility with local terrains and regulations is vital.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure safety and performance in group rides. This includes routine checks of the engine, brakes, and tires.
For ATVs and Side by Sides, maintaining proper tire pressure and inspecting suspension systems are crucial. U.S. Forces may implement strict schedules to ensure readiness and reliability.
Detailed records of inspections and repairs improve longevity. Using a checklist or database aids in tracking wear and replacements. Emphasizing preventative maintenance reduces downtime and prevents accidents. Spare parts and tools should be readily available during rides, mirroring the practices of military operations that require prompt responsiveness.
Safety Gear and Accessories
Safety gear is non-negotiable for ATV and Side by Side riders. Helmets, gloves, goggles, and protective clothing should be worn at all times to minimize injury risks. In military scenarios, additional protection may include ballistic gear depending on mission parameters.
Accessories enhance the ride experience and safety. GPS systems, radios, winches, and lighting are vital for navigation and communication. These tools are critical in environments where coordination and visibility are paramount. Comparing safety protocols with those of NATO and U.S. Forces highlights the focus on gear that enhances operational effectiveness.
Tactical Considerations
Successful group riding in ATV formations and Side by Side convoy practices involves strategic planning and tactical awareness.
Key elements include efficiently using terrain, selecting optimal formations for hostile situations, and employing evasion tactics to counteract sabotage.
Utilizing Terrain and Cover
Terrain plays a critical role in the tactical operations of ATVs and Side by Sides. Using natural cover like dense foliage or elevation changes can help evade detection by insurgents or guerrilla forces.
Operating in areas that provide natural barriers aids in avoiding direct fire from anti-tank weaponry.
Techniques:
- Elevation: Use high ground for better visibility and strategic advantage.
- Natural Barriers: Leverage trees, rocks, or hills for immediate cover.
These methods can greatly enhance the operational success of a battalion or company C in executing missions efficiently.
Formation Strategies in Hostile Environments
In hostile environments, choosing the right formation is crucial for safety and mission efficiency. A staggered formation can minimize exposure to hostile fire and IEDs, while maintaining a coherent unit structure.
Task Force Reaper stresses tight unit cohesion for swift shifts in tactics.
Common Formations:
- Staggered: Best for uneven terrain and provides flexibility.
- Column: Ideal for narrow paths, but requires vigilance at front and rear.
Such organized formations are critical for coordinating movements in and around base camps or when facing adversaries equipped with howitzers.
Evasion and Counter-Sabotage Tactics
Evasion techniques are essential to counter-sabotage efforts, particularly in areas prone to guerrilla warfare. Maneuverability and speed are key assets of ATVs and Side by Sides, allowing them to quickly alter paths or formations to avoid ambushes or minefields.
Tactical Actions:
- Counter-Surveillance: Frequent stops to check and alter routes.
- Diversion Tactics: Creating noise or decoys to mislead insurgents.
Task Force Reaper employs these tactics effectively to secure success and minimize casualties. These strategies are vital for units such as those in I Corps to adapt during missions against well-entrenched hostiles.
Historical Context and Evolution

The origins of group riding in military contexts have shaped modern ATV formation guidelines. Tactical advancements during major military conflicts have also influenced Side by Side convoy practices.
Group Riding in Military History
During World War II, coordinated vehicle formations became critical for effective troop movement. The Marine Corps perfected these formations, emphasizing precision and discipline.
Military vehicles were often organized in columns to improve communication and strategic flexibility. This approach was particularly vital during amphibious operations, where coordination with aircraft support ensured comprehensive tactical coverage.
In the Cold War, the necessity for rapid deployment and operational readiness led to further development. Techniques were refined to accommodate new technology, such as the introduction of the AK-47, which impacted infantry mobility.
These historical lessons in group riding have directly influenced modern ATV and convoy arrangements, prioritizing safety and efficiency.
Advancements in Tactical Vehicle Use
The Vietnam War further introduced innovations as the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) and U.S. forces utilized tactical vehicles for diverse terrains. Integration with brigade combat teams highlighted the need for versatile and adaptive vehicle formations.
Advancements in engineering during this era enhanced vehicle speed and protection. These improvements supported more complex convoy practices, merging traditional military precision with emerging technologies.
The historical evolution of tactical vehicle use continues to inform contemporary practices in both ATV and Side by Side formations.
Training and Simulation

Training and simulation are vital to mastering group riding techniques, enhancing safety, coordination, and skill. These methods help participants prepare for real-world conditions, ensuring both beginners and advanced riders can navigate formations effectively.
Simulated Exercises for Group Riding
Simulated exercises provide a controlled environment where riders can practice both ATV and Side by Side convoy formations. Military installations like Fort Benning utilize such simulations to reinforce safety and coordination among their trainees.
These exercises often mirror real-world conditions, including terrain changes, obstacles, and varied weather patterns.
Participants learn critical skills such as maintaining speed consistency and communication, which are essential in group riding settings.
Simulated scenarios can be adjusted to increase complexity gradually, enhancing the learning curve while prioritizing safety.
ATVs and Side by Side vehicles require specific formation adjustments. Regular role-playing in these scenarios benefits both novice and experienced riders, contributing to cohesive group movement and effective decision-making in unpredictable environments.
Skill Development and Progression
Focusing on skills development and progression ensures that riders are well-prepared for actual group riding situations. The U.S. Army employs structured training programs like Advanced Individual Training (AIT) to develop vehicular operation skills.
This robust approach underscores the importance of consistent practice and gradual skill elevation.
In civilian contexts, progression begins with fundamental maneuvers before advancing to more challenging tasks. Incremental skill-building promotes confidence and competence, vital for safe riding in group formations.
Training includes exercises such as obstacle navigation, communication techniques, and maintaining formation integrity.
Practical experiences combined with feedback from instructors foster an environment conducive to continuous improvement. This methodology ensures riders are adequately equipped with the skills necessary to excel in both individual and group riding endeavors.
Legal and Safety Regulations
ATV group riding and side-by-side convoy practices require awareness of specific legal and safety regulations. Compliance with national military standards and adherence to operational safety protocols are crucial for minimizing risks during such activities.
Compliance with National Military Standards
When organizing ATV group rides, compliance with national military standards is essential, particularly for those operating on or near military installations.
The Ministry of National Defense enforces regulations that may include vehicle specifications, permitted areas, and approved formation tactics.
All drivers must ensure their vehicles meet specified safety standards. This includes regular maintenance and inspections.
Those involved should be familiar with MOS (Military Occupational Specialty) guidelines, which can dictate equipment operational skills.
Permits may be required, particularly in restricted military zones. It’s important to coordinate with military authorities to secure necessary approvals and align with their protocols.
Operational Safety Protocols
Operational safety during group rides is paramount.
Riders in formation should follow guidelines, such as maintaining a safe distance and communicating effectively through hand signals or communication devices.
Every participant should wear adequate protective gear, including helmets and gloves, to reduce injury risks.
Organizationally, a lead and sweep rider should be designated to manage pace and keep track of the group’s integrity.
Regular briefings on route plans and emergency procedures are advisable.
Understanding the terrain and environmental conditions can greatly impact the safety and efficiency of the ride.
It’s vital to ensure that all riders are equipped with essential supplies, including navigational tools and first-aid kits.