As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
The world of off-road vehicles offers a thrilling experience, but mastering them requires distinct approaches.
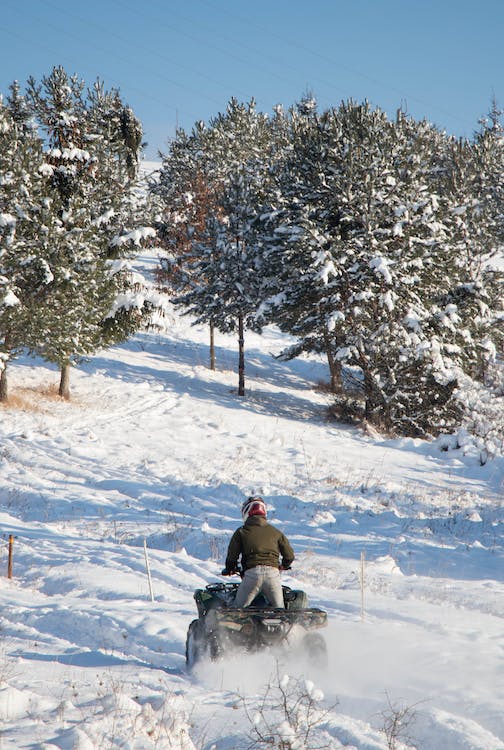
Skill progression for ATVs focuses on individual technique development. It emphasizes balance, control, and maneuverability in various terrains. These personal skills are crucial for safe and enjoyable rides, as they empower the rider to handle unexpected obstacles and changing conditions effectively.

In contrast, driving a Side by Side vehicle involves different responsibilities due to shared operation dynamics.
Side by Side responsibility stages include communication and teamwork, especially when multiple occupants are involved. The driver not only manages vehicle control but also ensures passenger safety and comfort, highlighting the importance of leadership and coordination skills.
Understanding these vehicles and their unique demands enhances both safety and enjoyment. With clear distinctions between ATV techniques and Side by Side responsibilities, enthusiasts can tailor their learning to suit their vehicle of choice, maximizing both fun and safety on the trails.
ATV Technique Fundamentals
Developing ATV technique fundamentals involves grasping key mechanical concepts, mastering basic riding skills, and adhering to essential safety protocols. These elements ensure a well-rounded foundation for any ATV rider.
Understanding ATV Mechanics
An All-Terrain Vehicle (ATV) operates uniquely, requiring familiarity with its mechanics. The rider should understand the function of the throttle, brakes, and gear shifts.
Being aware of how these interact on varying terrains is crucial. Unlike cars, ATVs use body weight distribution for steering and balance. The rider must lean appropriately based on the terrain to maintain stability.
A basic knowledge of engine maintenance prolongs vehicle life and ensures safety. Regular checks of oil levels, tire pressure, and brakes are essential. Also, adhering to guidelines by organizations like the CPSC ensures compliance with safety regulations.
Basic Riding Skills
Basic skills are pivotal for confidence and control. Starting with mounting the ATV correctly involves maintaining balance and positioning oneself centrally.
Once mounted, maintaining a neutral position when on flat surfaces and adjusting your stance in response to terrain changes is crucial.
Making smooth starts and stops helps in managing control. Practice is key when learning turns; a rider should practice both fast and slow maneuvers.
Riding on different terrains, such as mud and gravel, prepares the rider for diverse conditions. Recognizing the importance of skill refinement can reduce accident risks, promoting a safer riding experience.
Safety Protocols and Gear
Safety is paramount in ATV riding, as not adhering to protocols can lead to serious injury. Wearing appropriate safety gear—helmets, gloves, and boots—is non-negotiable. Such equipment significantly reduces injury risks. Helmets should be DOT approved, ensuring maximum protection.
Understanding regulations, such as age restrictions and permissible riding areas, is essential for safe riding. The CPSC provides guidelines that help in minimizing accidents.
Adequate training is necessary; many regions require safety courses before riding publicly.
Health considerations, such as hydration and physical fitness, complement these protocols. A healthy rider can endure longer rides and react efficiently to unexpected challenges, reinforcing the importance of a comprehensive approach to safety.
Advanced ATV Techniques
Developing advanced ATV techniques enhances safety and performance across diverse landscapes. Mastering terrain navigation and improving speed and agility contribute significantly to a rider’s ability to traverse challenging environments responsibly.
Terrain Navigation
Effective terrain navigation is crucial for ATV riders facing diverse landscapes. Riders should prioritize understanding terrain types, including rocky paths, muddy trails, and forested areas. This is vital for maintaining control and reducing impacts on sensitive environments like wildlife habitats.
Riders can use a terrain map to identify potential hazards, such as sharp inclines or water crossings. Skills like reading the terrain and anticipating changes in ground conditions support safer riding.
When navigating slopes, balance is key. Shifting weight appropriately and maintaining slow speeds prevent accidents and reduce soil erosion.
Carrying essential tools, such as a GPS device and compass, ensures precise navigation and location tracking. Terrain awareness also helps minimize disturbances to local ecosystems, promoting responsible recreation.
Speed and Agility Training
Speed and agility training enhances an ATV rider’s capacity to react quickly to unexpected obstacles. Training programs often incorporate sprints, slalom courses, and other drills to improve reflexes and dynamic control.
Riders should balance acceleration with maneuverability to maintain stability on uneven ground. Practicing rapid turns and controlled stops on different surfaces cultivates a keen sense of timing and spatial awareness.
Developing this skill set requires disciplined practice in both controlled environments and natural settings. A focus on safe, controlled increases in speed ensures that riders remain aware of their surroundings, minimizing the potential to disrupt wildlife habitats or cause erosion. Consistent training builds confidence and precision in high-speed scenarios.
Maintenance and Preparation

Proper maintenance and preparation ensure that all-terrain vehicles (ATVs) and side-by-side vehicles perform efficiently and safely. Adhering to regular care routines enhances vehicle longevity and reduces the chances of malfunctions on trails. Each type of vehicle requires specific attention to detail and a keen eye for safety to yield the best results.
ATV Care and Upkeep
Regular maintenance of ATVs involves several critical steps. Oil changes should be consistent to ensure engine parts remain lubricated and function as intended. Checking the air filter for debris and wear is vital, as it improves performance and fuel efficiency.
Maintaining the tire pressure optimizes both safety and traction, especially on varied terrains.
Brake inspections help identify wear and prevent potential failures. Don’t forget to periodically examine the battery connections for any corrosion, possibly extending battery life.
Rotating and applying a fresh coat of lubricant on the chain, if applicable, keeps it functioning smoothly without unnecessary wear.
Pre-Ride Inspections
Conducting a thorough pre-ride inspection is an essential habit for safety and reliability. Start with a visual check of tire integrity, looking for punctures or cuts.
Confirm that the lights and signals are operational, ensuring visibility and communication with other riders. The brake and throttle response must feel right; unresponsiveness could indicate the need for immediate service.
Take time to inspect fluid levels such as oil, coolant, and brake fluid. Verifying the tightness of bolts and fasteners can prevent mechanical failures.
Having a basic repair kit on hand provides peace of mind to address minor issues before they escalate into problems on the trail.
Side by Side Responsibility Basics

Operating a Side by Side vehicle requires awareness of specific features and an understanding of rider safety protocols. Key areas include the vehicle’s mechanical attributes and essential safety practices.
Understanding Side by Side Features
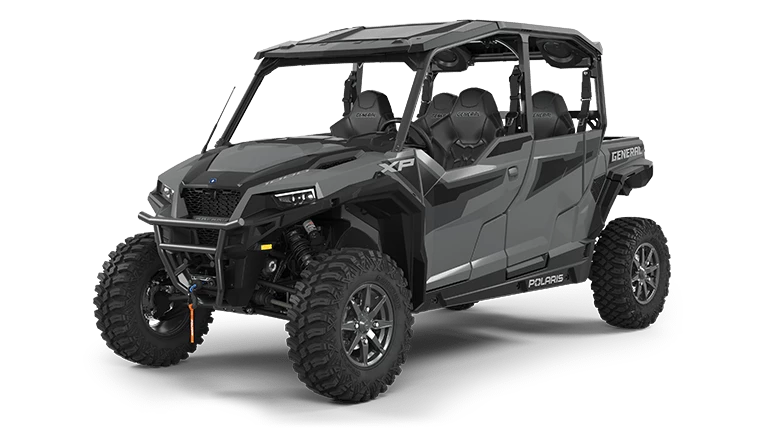
Side by Side vehicles, also known as UTVs (Utility Task Vehicles), offer unique features distinct from traditional ATVs. Engine size, cargo capacity, and seat arrangements are specific to these vehicles. They often have higher weight limits, allowing for multiple passengers and gear.
Individuals must acquaint themselves with key components such as roll cages, doors, and seat belts. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) often provides guidelines on modifications and structure enhancements.
Familiarity with state and local regulations is critical. Laws vary regarding age restrictions, vehicle registration, and terrain access. Not adhering to these can lead to fines or more severe penalties. Understanding these features and rules ensures a more responsible and informed driving experience.
Rider and Passenger Safety
Safety remains paramount when it comes to Side by Sides. Both drivers and passengers must wear appropriate safety gear, which includes helmets, gloves, and closed-toed footwear.
Seat belt use is mandatory for all occupants to prevent injuries in case of an accident or sudden jolt.
Passenger size and weight limits must be adhered to as specified by manufacturers. Exceeding these can compromise vehicle stability.
Ensuring all passengers are securely seated and within appropriate height limits helps prevent them from falling or being ejected.
Safety training courses are often recommended. They cover critical areas such as emergency maneuvers, vehicle handling, and off-road navigation. Proper training can significantly reduce accident risks and enhance the overall driving experience.
Role of Side by Side in Outdoor Recreation

Side by Side vehicles have transformed outdoor recreation by providing more inclusive access to diverse terrains. They enable adventure enthusiasts to explore remote landscapes with ease while maintaining environmental respect and trail etiquette.
Environmental Considerations
Operating Side by Sides involves understanding their impact on natural habitats. The Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management often regulate areas where these vehicles can travel, ensuring minimal disruption to local ecosystems.
Tread Lightly! principles encourage recreationists to ride only on designated trails, reducing soil erosion and protecting wildlife.
Recreational areas, when managed properly, offer a balance between enjoyment and conservation. Operators should inspect and maintain their vehicles regularly to prevent oil leaks and reduce carbon emissions, thereby preserving the environment. Sustainable driving practices ensure these recreational pursuits can continue without harming nature.
Trail Etiquette and Usage
Adhering to trail etiquette is crucial when using Side by Sides in outdoor settings. Establishing good rapport with other trail users like hikers, cyclists, and horse riders fosters a cooperative environment.
Yielding right of way, maintaining safe speeds, and using hand signals contribute to a safer and more enjoyable experience for all.
Trail-sharing policies promoted by public land agencies like the Bureau of Land Management emphasize mutual respect. Side by Side users should stay informed about trail-specific regulations and closures to ensure compliance. These practices help protect trails, maintain community relationships, and facilitate a positive recreational experience.
Special Considerations for Professional Use

Professionals using ATVs and Side by Sides face unique demands and responsibilities. They must prioritize safety standards and leverage specialized equipment features to ensure efficiency and compliance in their work environments.
Using ATVs and Side by Sides for Work
ATVs and Side by Sides provide significant advantages in various work settings, such as agriculture, construction, and maintenance tasks.
They offer enhanced mobility and the ability to access difficult terrains, making them invaluable for transporting materials and equipment.
Their compact size and maneuverability allow them to navigate narrow spaces and reach areas inaccessible to larger vehicles.
When considering equipment choices, it’s crucial to evaluate the specific demands of the job, environmental conditions, and the health and safety of workers.
Proper training ensures that workers operate these vehicles efficiently, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Compliance with Safety Standards
Operating ATVs and Side by Sides professionally requires strict adherence to established safety standards.
Compliance includes wearing appropriate protective gear, such as helmets and gloves, and ensuring regular vehicle maintenance.
Vehicles must be inspected frequently to maintain peak performance.
Employers are responsible for providing comprehensive training programs that cover safety protocols, risk management, and emergency procedures.
Understanding local and national regulations surrounding off-road vehicle use is essential to avoid legal issues and protect worker health and safety.
Organizations should also conduct periodic safety audits and assessments to continuously improve practices and adapt to any regulatory changes.