As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
Navigating the world of off-road vehicles requires understanding both ATV technique development and the essential stages of Side by Side (SxS) responsibility. Each type of vehicle presents its own unique challenges and skills to master, yet enthusiasts should embrace these as opportunities to grow their abilities.
Developing distinct techniques for ATVs and understanding the responsibility stages in Side by Sides is crucial for safe and effective riding.

The distinction between All-Terrain Vehicles (ATVs) and Side by Sides lies in their handling and operational guidelines. While ATVs demand mastery of balance and terrain adaptability, Side by Sides emphasize awareness and cooperative management due to their larger size and passenger capacity.
Both vehicles require a focused dedication to skill enhancement to ensure safety and proficiency.
As riders advance their skills, they must appreciate the diverse applications and responsibilities across different terrains and environments. With the right approach and informed techniques, both ATV riding and Side by Side driving can become more than just recreational hobbies—they offer a broader understanding of off-road exploration and personal growth.
Fundamentals of ATV Riding

Mastering ATV riding involves a deep understanding of vehicle mechanics, adherence to safety precautions, and awareness of health implications. Each aspect is essential for both a pleasurable and secure outdoor recreation experience.
Understanding ATV Mechanics
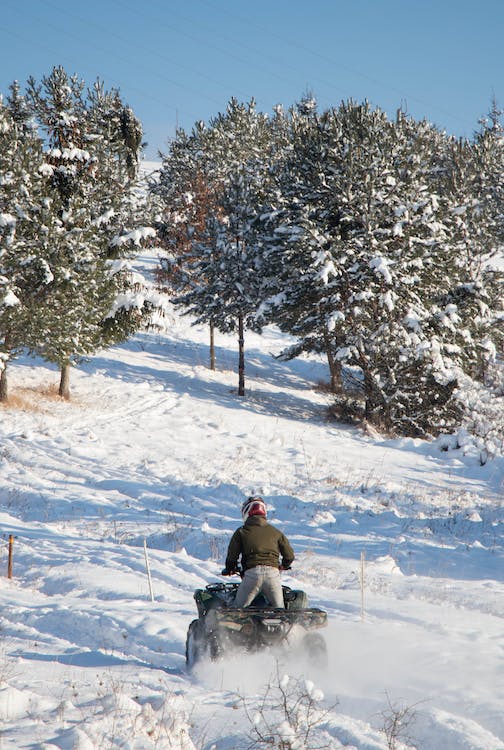
All-terrain vehicles (ATVs) are unique in their design and functionality. They come equipped with low-pressure tires, which provide stability across various terrains. The engine, typically between 49cc and 1,000cc, determines power and is crucial for adjusting speed appropriately.
Riders must familiarize themselves with throttle controls, braking systems, and gear shifts. Knowing the effect of differential locks and how suspension works can optimize performance.
Understanding these components ensures efficient operation for recreational or work-related tasks.
Consulting the owner’s manual can provide specific insights into maintenance and troubleshooting problems, creating a reliable and smooth riding experience. Knowledge in these areas is especially vital for preventing mechanical failures during outdoor excursions.
ATV Riding Safety Precautions
Safety in ATV riding should never be compromised. Wearing specialized gear such as helmets, gloves, boots, and goggles reduces the risk of injury. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) strongly recommends protective equipment.
Inexperienced riders should pursue training courses. Certified courses teach proper handling, risk assessment, and accident avoidance techniques.
Staying sober is also critical since alcohol impairs judgment and reaction time.
Trail etiquette is essential—alert others to your presence and reduce speed in crowded areas. Operating an ATV in harsh weather, like rain or snow, demands extra caution. Observing these precautions safeguards against common accidents and promotes a safe and enjoyable experience.
Health Considerations in ATV Riding
ATV riding requires physical and mental readiness. Maneuvering an ATV involves core strength and endurance, particularly during extended rides.
Warm-up exercises can prepare muscles for the physical demands, reducing the chance of strains or sprains.
It’s vital to stay hydrated and take regular breaks. Prolonged rides without rest periods can lead to fatigue, which raises the risk of mishaps.
Riders should also consider the stress ATV riding may put on joints, especially with older or pre-existing health conditions. Consulting with a healthcare provider can clarify any concerns about potential risks linked to ATV recreation activities.
ATV Technique Development
Skill development in ATV riding progresses through understanding fundamental techniques, honing intermediate strategies, and mastering advanced maneuvers. Each stage builds on the previous, offering riders unique challenges and growth.
Beginner Techniques and Skills
New ATV riders start with basic skills essential for safety and enjoyment. They focus on learning proper body positioning, which includes maintaining balance through correct posture and weight distribution. Navigating flat terrains helps to practice throttle control and braking.
Safety is emphasized through the use of protective gear, including helmets, gloves, and appropriate clothing. Beginners also familiarize themselves with vehicle controls and basic maintenance, such as checking tire pressure and oil levels.
Understanding environmental conditions and how they can affect riding is crucial at this stage.
Intermediate Riding Strategies
Intermediate riders develop a deeper understanding of how to handle varied terrains, such as hills, mud, and sand. Techniques like standing on the footrests while ascending or descending slopes increase stability and control.
Riders begin to execute more precise turns using body lean and throttle control, with S-turns and figure eights as common practice drills. Risk assessment becomes more advanced, incorporating weather conditions and obstacles into decision-making processes.
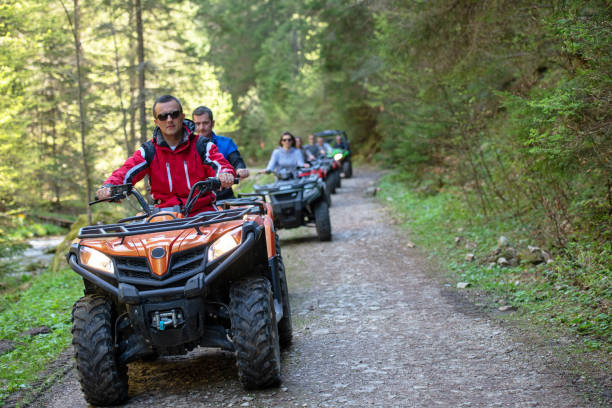
This stage often includes group riding, requiring coordination and adherence to group signals.
Advanced ATV Maneuvers
Advanced riders master complex maneuvers, which demand high levels of precision and confidence. Skills such as traversing rocky terrains and handling steep, uneven slopes without losing control are developed.
Technical moves like wheelies or controlled slides require perfected throttle modulation and balance.
Advanced training often includes competitive scenarios, where riders engage in obstacle courses or races, pushing their skills to the limit. Riders also refine emergency response techniques, enabling quick reaction to unexpected situations or equipment failures.
Side by Side Responsibility Stages

The responsibility stages in Side by Side vehicle operation encompass understanding vehicle functions, adhering to safety standards, and addressing environmental impacts. Operators must be well-versed in the technicalities of the vehicle and the obligations to the land they traverse.
Introduction to Side by Side Vehicles
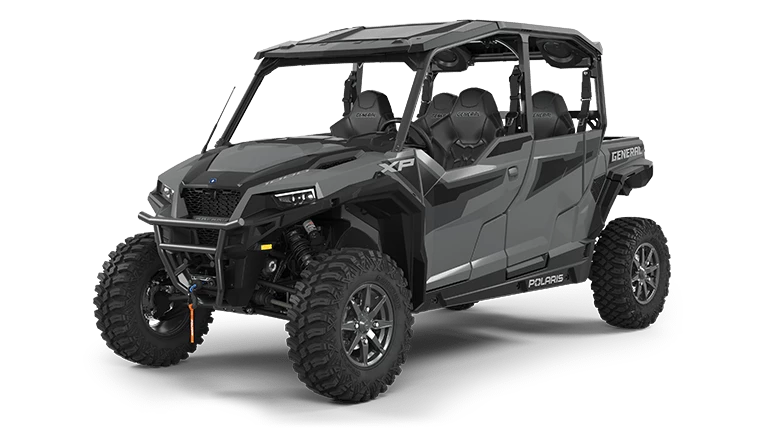
Side by Side vehicles, often referred to as UTVs, are designed to carry passengers alongside the driver. They provide benefits like increased stability and greater load capacity. Users must be familiar with steering mechanisms, seating layouts, and cargo holds.
Safety enhancements make these vehicles suitable for diverse terrains. They often include roll cages, seat belts, and robust suspension systems, emphasizing protection and control.
Proper knowledge of vehicle mechanics helps operators handle the tasks they are designed for, along with operating the vehicle efficiently and responsibly.
Operational Responsibilities for Side by Side
Operators must adhere to specific safety regulations during the use of Side by Side vehicles. Wearing appropriate safety gear, such as helmets and gloves, is crucial. Operators should also check that all safety equipment is functioning correctly before use.
Awareness of local laws and regulations is critically important. Some regions may have specific rules governed by the Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management. The operational guidelines establish clear expectations for vehicle use.
Operators must follow best practices for passenger safety. This includes ensuring all passengers wear seatbelts and are briefed on safety procedures.
Environmental Stewardship and Side by Side
Operating Side by Side vehicles with environmental responsibility involves understanding their impact on wildlife habitats and soil. Respecting designated trails prevents soil erosion and protects natural landscapes. Operators should avoid veering off marked paths to minimize environmental impact.
Attention to wildlife is essential. Noise pollution from Side by Sides can disrupt habitats, so maintaining low noise levels is beneficial.
Practicing responsible use ensures minimal disturbance to the environment.
Compliance with regulations from organizations such as the Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management supports sustainable vehicle use. These practices preserve natural resources and contribute to long-term conservation efforts.
Regulatory Compliance and Best Practices

Regulatory compliance is essential for safe ATV operation and environmental protection. Best practices help protect riders and conserve natural areas. Understanding these regulations and adopting best practices ensures responsible and legal ATV use.
Understanding Local and Federal ATV Regulations
ATV riders must comply with both local and federal regulations. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) enforces safety standards, focusing on age restrictions and vehicle specifications. Federal laws often emphasize helmet use and prohibit operation on paved roads.
Local regulations vary and may include zoning rules and noise restrictions. Riders need to check with local authorities to understand specific requirements. Compliance prevents legal issues and enhances safety.
ATV Use in Environmental Conservation Areas
ATV riders must follow strict rules in conservation areas to protect wildlife habitats and prevent soil erosion. The Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management oversee these lands, enforcing regulations to minimize environmental impact.
Designated trails must be used, and speed limits followed to reduce disturbances to wildlife and minimize environmental degradation. Riders should educate themselves on local trail maps and environmental guidelines.
This ensures that ATV use in these sensitive areas aligns with conservation goals.
Safety Equipment and Gear
When operating ATVs or Side by Sides, using the right safety equipment is crucial. The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) emphasizes the importance of using up-to-date safety gear to reduce the risk of injuries. Riders should prioritize acquiring essential protective items and stay informed about the latest advancements in safety technologies.
Essential ATV Safety Gear
Riders should focus on acquiring helmets, gloves, and goggles. A sturdy helmet, preferably one meeting DOT or Snell standards, is critical for head protection. Gloves offer grip and protect hands from debris, while goggles shield the eyes from dust and branches.
Wearing long sleeves, pants, and over-the-ankle boots is also important. These items shield the body from scratches, abrasions, and minor impacts during rides.
The CPSC advises using brightly colored apparel to enhance visibility, which can be crucial when riding in areas with limited sightlines.
Up-to-Date Safety Gear Technologies
Staying informed about emerging technologies in safety gear is vital. Innovations such as advanced materials and impact-absorbing foams enhance protection and comfort.
Riders should look for gear that incorporates breathable fabrics and moisture-wicking properties to prevent overheating and maintain comfort during long rides.
Technological advancements have also led to the development of smart helmets with built-in communication systems. These features allow for effortless communication between riders, enhancing safety and coordination on trails.
Protective gear with integrated GPS and real-time tracking is becoming increasingly popular, offering additional layers of safety and connectivity for users.
Benefits of ATV and Side by Side Riding

The experience of riding ATVs and Side by Sides offers significant benefits from both a physical and mental perspective. Riders often experience enhanced fitness levels and mental well-being as they engage with these recreational vehicles.
Physical Health Benefits of Riding
Riding ATVs and Side by Sides can be a full-body workout. Steering, shifting, and maintaining balance engage the core muscles, arms, and legs.
Riders need strength and stamina, which can improve cardiovascular health and develop muscular endurance.
The outdoor aspect provides fresh air and sunshine, contributing to Vitamin D synthesis. Navigating challenging terrains can improve agility and reflexes, enhancing overall coordination and motor skills.
Mental Wellness and Outdoor Recreation
Outdoor adventures with ATVs or Side by Sides can boost mental health.
Engaging in outdoor recreation helps reduce stress and anxiety.
This form of activity encourages mindfulness and presence as riders focus on maneuvering through trails.
Taking rides through scenic landscapes can elevate mood by providing an opportunity to disconnect from daily pressures.
Engaging in this recreational activity can foster social connections, especially when riding in groups, enhancing a sense of community and well-being.
Professional Applications and Responsibilities
ATVs and side-by-sides serve vital roles in professional settings, including environmental management and various work environments. This section explores their specific uses and the responsibilities that come with operating these vehicles in professional contexts.
ATVs in Work Environments
ATVs are indispensable in many work scenarios, offering versatility and efficiency.
They are used in sectors such as agriculture, construction, and law enforcement. Workers rely on ATVs for quick transportation in areas where larger vehicles cannot navigate.
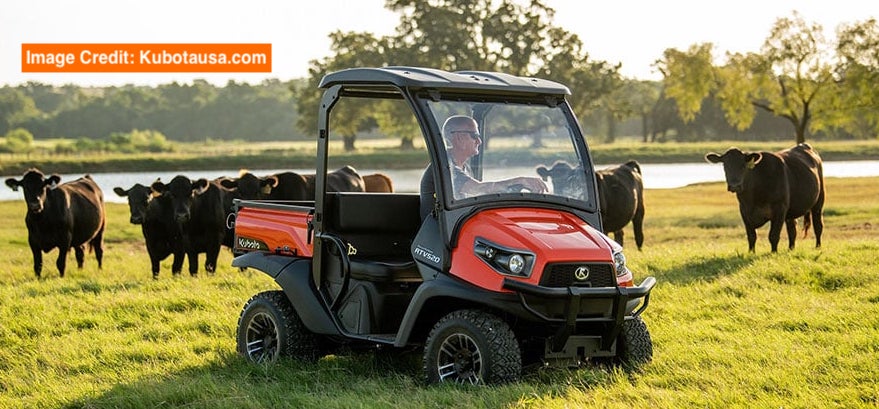
In agriculture, ATVs assist with tasks like monitoring livestock and inspecting crops.
Construction sites utilize them to transport tools and materials efficiently.
Law enforcement agencies employ ATVs for patrolling rugged terrains, ensuring safety in remote locations.
The ability to traverse rough landscapes quickly enhances productivity and effectiveness in these professional settings.
Roles of ATVs in Wildlife and Land Management
In wildlife and land management, ATVs play a crucial role in maintaining and surveying large areas.
Agencies like the Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management depend on them for tasks such as habitat assessments and land maintenance.
These vehicles allow wildlife officers to access and monitor remote areas efficiently.
ATVs are used to transport equipment essential for land restoration projects and to navigate dense forests without causing significant environmental disruption.
Their ability to move swiftly across various terrains supports conservation efforts and aids in the management of public lands.