As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
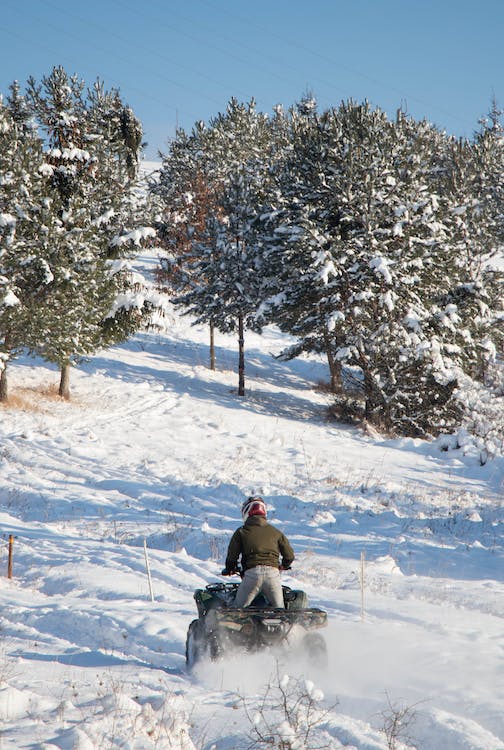
Sound profiles in off-road vehicles have become an intriguing subject for enthusiasts and casual listeners alike. The auditory distinction between a 2-stroke ATV engine and a 4-stroke Side by Side is especially fascinating.
The 2-stroke ATV is known for its high-pitched, buzzy sound, contrasting sharply with the deeper, more mellow rumble of a 4-stroke Side by Side.

These differences are not only auditory but also functional, reflecting the mechanics and performance of each vehicle type.
Two-stroke engines, due to their design, emit a distinctive whine that can be equated to a fast-paced, energetic note. In contrast, 4-stroke engines give off a thrum that’s more aligned with steady power and reliability, appealing to those seeking a quieter ride.
Understanding Sound Profiles
Sound profiles involve examining characteristics of how engines generate and project noise. Different engines, like the 2-stroke ATV and 4-stroke Side by Side, produce distinct sound environments with unique qualities such as pitch, tone, and resonance.
Fundamentals of Sound Generation
Engine sound creation begins with mechanical movements and exhaust emissions.
Compression impacts noise intensity as pistons compress air-fuel mixture. Meanwhile, resolution refers to how clearly individual sound features can be discerned, highlighting elements like exhaust beats.
Soundstage describes the perceived space from which sound emerges, influencing how an engine’s noise fills and interacts with its surroundings. Together, these elements define the acoustic signature of different engine types, offering an auditory experience unique to each platform.
Characteristics of ATV and Side by Side Acoustics
2-stroke ATVs are known for their high-pitched, intense sound profiles. These engines accentuate vibrations and rapid exhaust pulses, creating an energetic noise experience. The sound resolution may reveal sharp, distinct beats given quick compression cycles.
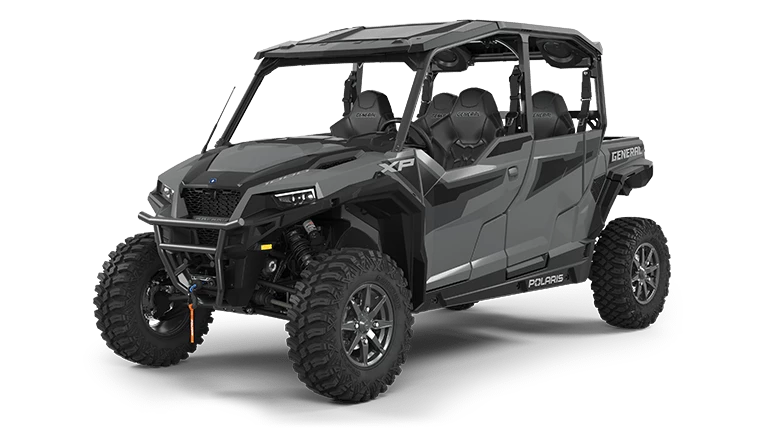
The 4-stroke Side by Side vehicles typically have a deeper, more rumbling tone, characterized by four distinct strokes per cycle. This results in smoother sound waves with a broader soundstage, filling an expansive auditory space. Engine compression contributes to a mellow acoustic quality, distinguishing these vehicles’ sound profiles from their 2-stroke counterparts.
2-Stroke ATVs
2-stroke all-terrain vehicles (ATVs) produce a distinct and recognizable sound pattern due to their specific engine design. Known for their lightweight and powerful performance, these machines are often preferred in various recreational activities. The impact on the environment and the different characteristics of their sound production are explored.
Mechanism of Sound Production in 2-Stroke Engines
2-stroke engines produce sound from several technical operations: intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes. Unlike 4-stroke engines, they complete a power cycle in just two movements of the piston.
This results in a higher frequency of ignition events, producing more noise. Meanwhile, torque is distributed differently due to this rapid cycling, resulting in a characteristic sharp and high-pitched sound. Noise levels are amplified because both the exhaust and intake operations occur almost simultaneously.
Advantages and Limitations of 2-Stroke ATVs
2-stroke ATVs are favored for their simplicity, reduced weight, and excellent power-to-weight ratio. This makes them ideal for applications requiring rapid acceleration and maneuverability.
They require less maintenance and generally have a more straightforward ignition system. However, they consume more fuel and produce more emissions, which can affect compliance with EPA regulations. Despite their performance benefits, the environmental impact and noise pollution are significant considerations.
Impact of 2-Stroke Sound on Environment
The distinct noise from 2-stroke ATVs contributes to environmental noise pollution. These engines release more unburned fuel and oil as part of their exhaust, which not only impacts air quality but adds to the overall sound emissions.
Regulatory bodies like the EPA have set standards to limit these effects. Restrictions on noise levels are enforced in various regions to minimize the impact on local wildlife and residential areas. As a result, the use of 2-stroke engines is declining in heavily regulated areas.
4-Stroke Side by Sides

4-stroke side by sides offer a unique sound signature distinct from other engine types. With a focus on performance, they balance horsepower and noise control, making them a favorite for many off-road enthusiasts. Their environmental impact is also a key consideration, with compliance to regulations like the EPA’s.
Sound Signature of 4-Stroke Engines
4-stroke engines are known for their steady and consistent sound. Unlike the high-pitched, rapid-fire noise of 2-strokes, 4-strokes produce a lower, more laid-back hum. This is due to their complete combustion cycle, which includes intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes. The result is a smoother and less aggressive auditory experience.
The sound level of a 4-stroke side by side can vary based on the engine’s size and tuning. Many manufacturers are designing engines to keep noise levels within acceptable limits while still ensuring performance. Custom exhaust systems and sound dampening materials can further reduce noise, catering to those who prefer quieter rides.
4-Stroke Engines: Performance and Noise Control
Performance in 4-stroke side by sides is characterized by a balance of power and efficiency.
4-stroke engines offer higher torque at lower RPMs, which can translate into superior off-road capabilities. Horsepower ratings can vary widely but typically range from 50 to over 200, depending on the model and purpose.
Noise control is crucial, especially for enthusiasts concerned about community regulations and personal preference.
By utilizing advanced muffler designs and engine insulation, manufacturers can reduce the noise output remarkably. This balance between power and quiet operation makes 4-strokes appealing for both recreational and utility-oriented users.
Environmental Considerations for 4-Stroke Side by Sides
4-stroke engines are generally more environmentally friendly compared to their 2-stroke counterparts. They are designed to meet stringent emissions standards set by agencies like the EPA.
This is achieved through efficient combustion and cleaner exhaust systems, which reduce the release of pollutants.
Proper maintenance is vital to keeping emissions low. Regular oil changes and air filter replacements help maintain optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Users should also remain aware of local regulations and codes of practice (PROP) to ensure compliance. This serves the dual purpose of reducing environmental impact and maintaining good community relations.
Technical Comparison: 2-Stroke Versus 4-Stroke
Two-stroke and four-stroke engines differ significantly in engine technology, sound characteristics, and performance metrics such as torque and horsepower. The power curves of each type reveal insights into their respective capabilities and behavior under various conditions.
Engine Technology and Sound Characteristics
Two-stroke engines use combustion cycles involving intake, compression, power, and exhaust in just two strokes of the piston. The simplicity results in a louder, more aggressive sound profile typical of 2-stroke ATVs.
In contrast, four-stroke engines complete their cycle in four strokes. This approach reduces noise levels, creating a more subdued sound often heard in 4-stroke Side by Sides. The complexity of these engines leads to a smoother operation with quieter exhaust noise.
The distinct sound characteristics correlate with the differences in engine operation, affecting how these vehicles are perceived in terms of performance and user experience.
Performance Metrics: Torque and Horsepower
Two-stroke engines tend to produce higher power outputs relative to their size, offering significant horsepower advantages. However, they may exhibit less torque compared to their four-stroke counterparts.
In a four-stroke engine, torque is generally more consistent and plentiful across different RPMs, offering better control and stability. The horsepower in four-stroke engines builds more gradually, contributing to a steadier performance.
These differences underscore how each engine type delivers distinct dynamics suited for specific riding conditions and user preferences.
Comparative Analysis of Power Curves
Power curves offer a graphical representation of engine output across varying RPMs. Two-stroke engines often show sharp, peaking curves with sudden power delivery, benefiting high-speed performance scenarios but often resulting in abrupt driving experiences.
Four-stroke engines, with smoother, more linear power curves, provide steady acceleration. This design is advantageous for tasks requiring controlled power delivery, such as in rugged terrains where 4-stroke Side by Sides excel.
Examining the power curves on a dyno reveals these dynamics and illustrates the practical implications of their design, offering insight into how each engine aligns with users’ performance expectations.
Measuring and Analyzing Noise Levels
Measuring the noise levels of 2-stroke ATVs and 4-stroke Side by Sides involves specific techniques. The analysis of this data helps understand their impact on the environment and human hearing.
Sound Level Measurement Techniques
Sound levels are measured using decibel meters, commonly known as sound level meters. These devices utilize microphones to capture sound pressure levels in the environment. To ensure accurate measurements, it’s crucial to calibrate the meters regularly and position them correctly relative to the sound source.
Equipment Choice is critical. High-resolution meters offer a more detailed analysis, capturing minute fluctuations in sound levels. Precision in placement and proper use of weighting filters, like A-weighting, tailor the reading to human hearing sensitivities. Consistent methodologies are essential for comparative analysis.
Interpreting Sound Level Data for ATVs and Side by Sides
Interpreting noise data involves comparing decibel levels across different vehicles.
2-stroke engines tend to produce a higher pitch and more abrupt sound signatures due to their engine design, which can be identified through peaks in their sound profiles.
4-stroke engines, on the other hand, emit a lower, more constant noise level. Decibel readings typically show less fluctuation for these vehicles. Analyzing these patterns helps determine compliance with noise regulations and can guide modifications to reduce environmental impact. Understanding this data assists enthusiasts and professionals in making informed decisions regarding vehicle usage and design adaptations.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance

Sound profiles of 2-stroke ATV engines and 4-stroke side-by-side vehicles are subject to specific regulatory standards.
These standards impact noise level restrictions and influence engine design choices.
EPA Regulations on Off-Road Vehicle Noise
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets noise emission standards for off-road vehicles, including ATVs and side-sides.
Regulations focus on protecting the public from excessive noise while maintaining environmental integrity.
Standards vary by vehicle type and intended use, with maximum permissible noise levels specified in decibels.
Manufacturers must ensure their vehicles do not exceed these limits during production.
Non-compliance can result in fines and halted sales.
The EPA conducts regular audits and tests to ensure compliance, promoting quieter, safer environments for recreational and work purposes.
Compliance and Impact on Engine Design
Compliance with noise regulations significantly influences engine design.
Manufacturers are required to balance performance with noise reduction technologies like advanced mufflers and sound-dampening materials.
These changes can affect engine efficiency and cost of production.
Incorporating quieter engine technology often involves adopting four-stroke engines over two-stroke options.
Four-stroke engines generally produce less noise, aligning better with EPA standards.
This shift can result in redesigned components to uphold power output while meeting legal noise requirements.