As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
Exploring the outdoors brings a chance to encounter wildlife, an experience that calls for responsible behavior, particularly when it comes to using off-road vehicles like ATVs and Side by Sides.
It’s crucial to understand how these machines impact wildlife and what can be done to minimize disturbances.
Implementing effective noise management in ATVs and promoting animal awareness for Side by Sides can significantly reduce negative interactions with wildlife.

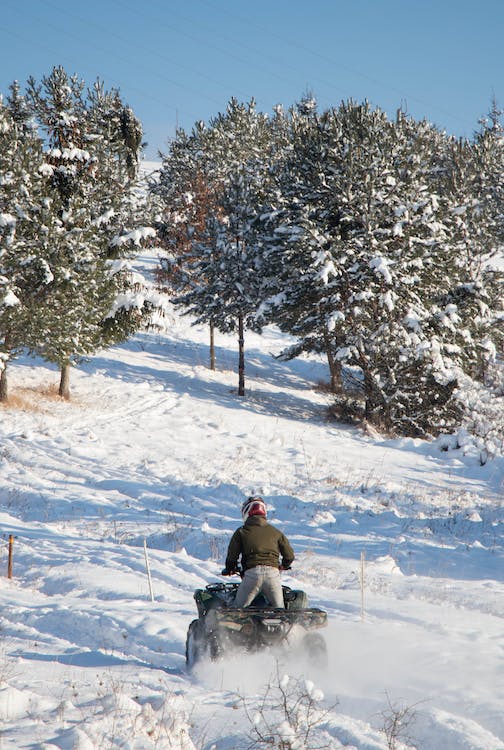
ATV noise management involves techniques and practices aimed at reducing the noise output of all-terrain vehicles, making trails quieter and less disruptive to animals.
On the other hand, Side by Side vehicles emphasize the need for drivers to be educated about the environments they traverse, ensuring they are alert and considerate of wildlife presence.
Both strategies provide a path to more harmonious coexistence with natural habitats.
By comparing and contrasting ATV noise management and Side by Side animal awareness, this article will examine these approaches’ effectiveness in preserving wildlife habitats. The goal is to inform outdoor enthusiasts about the best practices for enjoying nature while minimizing impact on the animals that inhabit it.
Understanding ATV and Side by Side Vehicles

Off-road vehicles like ATVs and Side by Side vehicles are popular for outdoor adventures. Their design and functionality cater to different needs and environments, with distinct impacts on wildlife habitats and management practices.
Characteristics of ATVs
All-Terrain Vehicles (ATVs) are designed for single riders and equipped with handlebar steering. They usually have a straddle seat, allowing the rider to shift their weight easily for better balance and control over rugged terrain.
ATVs are often used for recreational activity, hunting, or farm work. Known for their agility and lightweight design, they can navigate narrow trails and tight spots effectively.
Despite their advantages, ATVs can adversely affect natural habitats. Their compact size and weight distribution can lead to soil erosion, especially in sensitive areas. This impact requires careful management to preserve environmental integrity. Moreover, ATVs’ maneuverability can cause disruption in wildlife zones, necessitating mindful operation to minimize disturbances.
Characteristics of Side by Side Vehicles
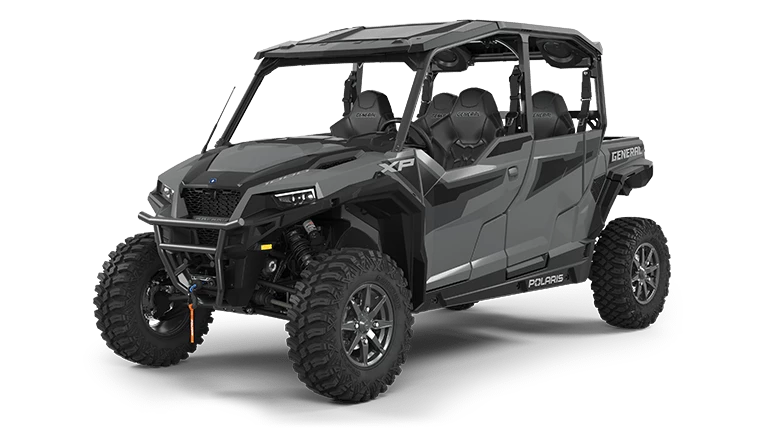
Side by Side vehicles, or UTVs, offer seating for two or more passengers, positioned side by side. They feature steering wheels and foot pedals, providing a more car-like experience.
Built for utility and power, these vehicles are ideal for transporting equipment and supplies. Due to their larger frame, they offer greater stability and comfort, making them suitable for longer journeys.
Their robust design allows them to handle challenging terrains, though their size can restrict access to narrow paths. Side by Sides can create significant habitat disturbances, especially when used off designated trails. Effective management strategies are necessary to ensure minimal adverse effects on the environment and wildlife.
Noise Produced by Off-Road Vehicles
Off-road vehicles, such as ATVs and Side by Sides, generate significant noise, which can have adverse effects on wildlife. The noise levels from these vehicles can disturb natural habitats, causing animals to flee or alter their behavior. This can disrupt feeding, breeding, and nesting patterns.
Noise management is crucial in areas where wildlife is present. Ensuring proper maintenance, using quieter models, or limiting operation times can help mitigate these impacts. Implementing designated trails and noise barriers are effective strategies to reduce auditory disturbances, helping to preserve local ecosystems.
Wildlife Behavior and Sensory Perception

Wildlife responds uniquely to noise and environmental changes. Animals’ hearing capabilities and their reaction to various noises play key roles in understanding their behavior.
Animal Hearing and Reactions to Noise
Animals possess diverse hearing sensitivities affecting their reaction to human-made noises like those from ATVs and Side by Side vehicles. Deer, for example, can detect subtle sounds which alert them to potential threats.
Noise disturbances can lead to increased stress levels and altered behaviors in wildlife. These changes might include altered feeding patterns or avoiding certain areas.
It’s crucial for conservation efforts to consider these sensory sensitivities. Reducing noise pollution helps minimize negative impacts on wildlife, allowing them to maintain natural behaviors and territorial activities.
Animal Territory and Movement
Territorial behavior is essential for many animals, guiding their interactions and movements within their habitats. Different species establish territories using sensory cues and vocalizations to mark boundaries.
Excessive noise can disrupt these territorial patterns, prompting animals like deer to relocate.
Noise interference with territory can lead to increased competition and altered feeding habits. Such disruptions may force wildlife to enter less favorable areas, impacting their survival and reproductive success. Preserving natural territories is vital to maintaining ecological balance.
Wildlife Communication and Vocalizations
Wildlife communication relies heavily on vocalizations which can be hindered by ambient noise. Deer, birds, and other species use calls to communicate warnings, attract mates, and establish territories.
Increased noise levels from recreational vehicles can mask these vital calls, leading to communication breakdowns.
Effective communication is fundamental for mating success and predator avoidance. Disturbances in this system can affect population dynamics and animal interactions. Reducing noise emissions from recreational activities helps ensure that wildlife can effectively communicate within their ecosystems.
Environmental Impact of Off-Road Vehicles
Off-road vehicles, such as ATVs and side by sides, can significantly affect natural habitats in several ways. Their use often leads to habitat disruption, influences animal behavior, and poses challenges for ecosystem management.
Habitat Disruption
The use of off-road vehicles in wilderness areas disrupts natural habitats. Trails created by these vehicles can lead to soil erosion, which further disturbs plant life. Vegetation loss not only affects plant species but also leads to habitat fragmentation.
The National Park Service often highlights that such disruption alters the landscape, making it difficult for plants to regrow and for animals to find viable habitats. These changes reduce biodiversity and impact various species that depend on a healthy environment. Effective trail management can help mitigate some of these issues.
Influence on Animal Behavior
Noise and movement from off-road vehicles affect animal behavior significantly. Species known for their sensitivity, such as birds and deer, may leave an area when exposed to these disturbances.
Studies conducted by biologists indicate these changes in behavior can disrupt feeding and mating routines.
For animals within national parks, such disruption can have long-term effects on population dynamics. Some species might adapt over time, but others may see declines in numbers if disturbances persist. This necessitates comprehensive wildlife management strategies to minimize impacts.
Ecosystem Management Considerations
Managing ecosystems with the presence of off-road vehicles is complex. Park managers must balance recreational use with conserving wildlife habitats.
Practices include designating specific areas for vehicle use to limit widespread environmental impact.
Tools like zoning, permits, and regular monitoring are used by organizations like the National Park Service to achieve sustainable management. These measures help to ensure that off-road vehicle activities do not undermine conservation objectives, allowing for both recreation and preservation objectives to be met.
Best Practices for Minimizing Wildlife Disturbances

Reducing the impact of off-road vehicles on wildlife involves effective noise management and understanding sensitive ecosystems. Responsible riding practices and strategic government regulations also play vital roles.
Noise Reduction Strategies
One effective approach is the implementation of quiet motor technology. Manufacturers are now developing engines with noise-dampening systems. Additionally, the use of modified exhausts can significantly reduce sound levels.
Noise barriers can also be strategically placed along trails to further minimize disruptions. Regulations by agencies like the National Park Service encourage this. Compliance with noise level guidelines ensures the protection of wildlife habitats while promoting public safety.
ATV and Side by Side Use in Sensitive Areas
When operating in ecologically sensitive areas, it’s crucial to limit the number of ATVs and Side by Sides. Designated trails help protect habitats while providing recreational opportunities.
The management of these trails is often overseen by government bodies like the National Park Service, which issues permits to control access. Seasonal restrictions ensure vehicles do not disrupt breeding or migration periods.
Riders should stay informed about area-specific rules, helping maintain sensitive landscapes.
Responsible Riding and Wildlife Protection Measures
Riders play a crucial role in wildlife conservation through responsible behavior. Educating users about maintaining slow and steady speeds can prevent abrupt disturbances to animals.
Keeping a safe distance from wildlife and avoiding known nesting areas further minimizes negative impacts. Regular training programs and workshops can raise awareness among riders.
Collaborative initiatives between wildlife agencies and riding clubs can promote these best practices effectively. Such partnerships can foster an environment where recreation and wildlife coexist harmoniously.
Wildlife Conservation and Public Safety

Wildlife conservation involves strategies designed to protect animal habitats while ensuring human safety. Addressing noise pollution, promoting awareness, and minimizing conflicts with wildlife like black bears are fundamental for harmony.
Protecting Animal Habitats
Noise pollution from vehicles such as ATVs and side-by-sides can disrupt natural habitats. Excessive sounds might alter the behavior of sensitive species. Implementing designated trails and noise regulations ensures minimal disturbance to wildlife. It is crucial for conservationists to collaborate with local authorities to enforce these measures effectively.
Electric fencing is another method to safeguard areas where noise restrictions may not be enough. Protecting animal habitats prevents illegal poaching and reduces stress in wildlife populations. Implementing quiet zones around breeding and nesting areas can promote biodiversity.
Promoting Public Awareness
Public awareness campaigns focus on educating outdoor enthusiasts about responsible behavior while exploring natural habitats.
Offering workshops and educational materials on the ecological effects of noise can foster understanding and respect for wildlife.
Signage along trails and interaction zones provides quick information about local wildlife and the importance of maintaining low noise levels. Encouraging participation in conservation initiatives, such as community clean-ups or bird counts, strengthens the bond between humans and nature.
Informed communities are better equipped to protect wildlife and contribute to ongoing conservation efforts.
Human-Wildlife Conflict Mitigation
Reducing human-wildlife conflicts is essential for safety and conservation. Conflict with species like black bears often arises from improper food storage and lack of awareness.
Utilizing bear-proof containers and educating the public on best practices reduces these incidents.
Electric fencing can prevent wildlife from entering human settlements, protecting both animals and people. Regularly monitoring conflict zones can help identify risks early and allow for proactive measures to be taken.
In areas prone to wildlife interactions, training sessions for residents on how to handle encounters calmly and respectfully are beneficial. Building community trust and engagement with wildlife authorities ensures safer cohabitation between humans and wildlife.
Regulations and Enforcement
Effectively managing noise from ATVs and ensuring wildlife conservation requires a robust legal framework and proper enforcement. National parks and other protected areas implement specific guidelines to balance recreation with habitat preservation.
Legal Framework for Wildlife Conservation
The National Park Service and other agencies enforce legal frameworks that prioritize wildlife habitat conservation.
Regulations stipulate permissible noise levels, trail access, and seasonal riding restrictions.
Legislation, such as the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), requires assessment of potential impacts on natural habitats before authorizing ATV routes.
These regulations aim to minimize disturbances to wildlife, ensuring their habitats remain undisturbed by excessive noise.
Public lands may have additional rules, including vehicle modifications to lower noise emissions and restrictions on group sizes.
These legal provisions underscore the commitment to preserving biodiversity within protected areas.
Enforcing Noise Limits and Riding Rules
Enforcement of noise limits and riding rules is crucial for minimizing disruptions to wildlife.
Park rangers and conservation officers play key roles in monitoring compliance. They use sound meters to measure decibel levels and ensure vehicles stay within the established limits.
Offenders face fines, vehicle impoundment, or removal from the area.
Education programs emphasize the importance of reducing noise and adhering to designated paths.
Cooperation between local law enforcement and federal agencies bolsters enforcement efforts.
Monitoring systems track compliance, and real-time reporting tools enable quicker response to violations.
Emphasizing education and awareness encourages riders to understand the significance of noise management in preserving natural habitats.
Future Directions in Vehicle Design and Wildlife Studies
Innovative approaches are being developed to address the impact of vehicles on wildlife.
These efforts focus on reducing noise from vehicles and improving methods to study animal behavior.
Innovation in Low-Noise Vehicle Technology
Vehicle manufacturers are prioritizing the reduction of noise emissions. Electric ATVs and side-by-sides offer a quieter alternative to traditional gas-powered models.
This innovation helps minimize disruptions to wildlife habitats.
Engineers are experimenting with acoustic management technologies, such as noise-canceling systems. These systems aim to mitigate sounds produced by engines and tires.
Reducing noise not only benefits wildlife but also enhances the experience for vehicle operators.
Collaboration between vehicle designers and biologists is crucial.
Designs are assessed for their impact on wildlife behavior. Through these partnerships, vehicle designs that effectively minimize adverse effects on ecosystems are being developed.
Advancements in Wildlife Monitoring and Research
Biologists are employing advanced technologies to study the effects of vehicle noise on wildlife.
Acoustic sensors and motion-activated cameras allow researchers to gather data on animal responses in real time.
Efforts to improve data analysis tools are underway.
Enhanced software helps in assessing noise impact by quantifying animal behavior changes. These tools are crucial for forming wildlife management strategies.
Researchers are increasingly utilizing drones equipped with sensors to monitor and track wildlife.
This technology enables the study of areas that are difficult for humans to access, providing valuable insights into animal habitats.