As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
When it comes to off-road recreation, water crossing methods present unique challenges for riders using quads and Side by Sides. Navigating through water requires careful consideration of each vehicle’s design and capabilities.
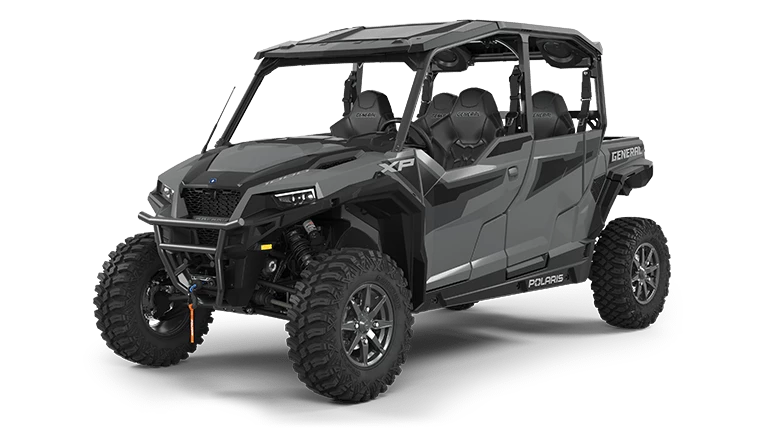
Side by Sides generally offer better depth advantages due to their robust build and higher ground clearance, making them suitable for deeper water crossings.

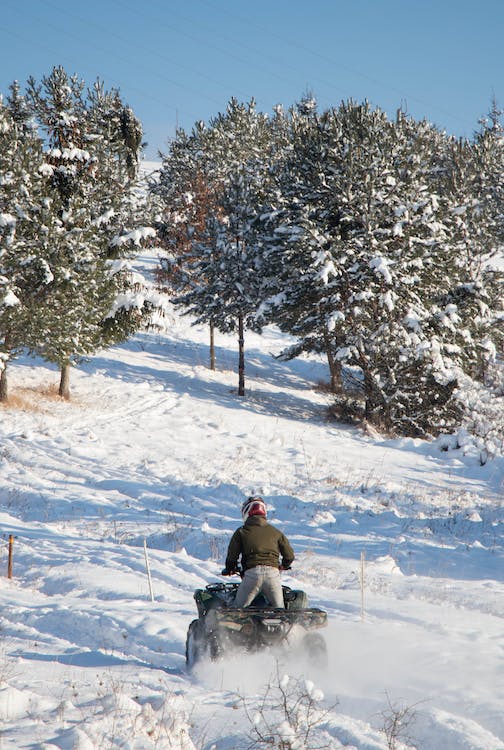
In contrast, ATVs, often referred to as quads, can face vulnerability concerns. Their lower center of gravity and open design may expose vital components to water damage. Riders must weigh these factors when selecting a vehicle for off-road adventures involving water.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of both ATVs and Side by Sides is crucial for safe and enjoyable riding. This knowledge equips enthusiasts with the insights needed to make informed decisions and maximize their riding experience.
Understanding Water Crossing Challenges
Navigating water crossings with ATVs and Side by Sides involves assessing their capabilities, considering environmental impacts, and ensuring adherence to management plans. These aspects are pivotal for safe and responsible driving.
ATV and Side by Side Basics
ATVs and Side by Sides offer unique features suited for off-road use. ATVs, also called quads, boast agility and can navigate narrower paths, but they are more vulnerable when faced with deep water crossings. Side by Sides, on the other hand, tend to handle deeper water better due to their enhanced stability and enclosed cabins.
Drivers must evaluate their vehicle’s specifications, including ground clearance and water fording depth. Understanding these aspects is crucial, as it dictates the type of water crossings each vehicle can undertake safely.
Erosion and Environmental Concerns
Erosion can result from repeated water crossings, which disrupts soil structure and increases sediment in water bodies. This erosion causes significant environmental impacts, including habitat disruption and water quality reduction.
These factors can adversely affect local ecosystems, leading to long-term degradation. Drivers must be mindful of the ecological footprint their activities leave behind. Avoidance of sensitive areas and following marked trails can help mitigate some of these issues.
Compliance with Management Plans
Compliance with existing management plans and federal agencies is essential for lawful water crossing activities. Such plans are designed to minimize environmental impacts and promote sustainable use of trails.
Regulations often outline permitted areas for crossing and conditions under which they can take place. Failure to comply can result in fines and further restriction of trail access. Thus, riders should familiarize themselves with all relevant guidelines and maintain open communication with authorities.
Comparative Analysis of ATVs and Side by Sides
A thorough comparison of ATVs and Side by Sides reveals design-based differences, depth navigation abilities, and their respective protection features. These vehicles are analyzed considering their unique attributes that affect performance, safety, and rider experience.
Design and Functional Differences
ATVs and Side by Sides possess distinct design elements. ATVs are typically smaller, lighter, and more agile, enabling riders to navigate challenging terrains with ease. This design emphasizes maneuverability and requires the rider to have a good sense of balance and control.
In contrast, Side by Sides are larger with side-by-side seating, offering more comfort and the ability to carry passengers or cargo. They often include features such as roll cages and roofs, enhancing protection during rides. This makes Side by Sides a popular choice for those prioritizing versatility and safety over compactness.
Depth Capabilities and Limitations
When it comes to water crossing, Side by Sides often have a depth advantage over ATVs. Side by Sides generally have a more elevated air intake, allowing them to tackle deeper waters without risking engine flooding. This design enables deeper water navigation with reduced risk of stalling or mechanical failure.
ATVs must exercise caution while attempting deeper water crossings due to their lower air intake position. Riders often find it necessary to gauge water depth meticulously to avoid potential engine damage. Ensuring the ATV stays operational during water crossings can be challenging given their limitations in deeper waters.
Protection and Support Features
Protection and safety are paramount concerns for both ATVs and Side by Sides. ATVs offer limited protective features, relying heavily on the rider’s gear for safety during an accident or collision. Helmets, gloves, and padded clothing are essential for minimizing injuries.
Side by Sides provide more built-in safety measures, such as roll cages, seat belts, and reinforced structures. These vehicles lessen the impact of collisions or rollovers, contributing to rider safety. The enhanced protection and support systems in Side by Sides cater to users who prioritize safety in their off-road experiences.
Safety and Training Considerations
Ensuring the safety of riders during water crossings involves understanding the necessary gear, training for the challenges of traversing water, and implementing practical accident prevention strategies. Proper preparation can significantly reduce the risks associated with navigating water on ATVs and side by sides.
Essential Riding Gear
Riders should prioritize wearing appropriate gear when engaging in water crossings. Waterproof boots are crucial to keeping feet dry and warm. Protective clothing like jackets and pants designed for water resistance help shield riders from the elements and potential injuries.
Helmets and goggles are vital for protecting against debris and providing clear vision. Gloves improve grip on controls, even when wet. Investing in quality gear reduces the risk of injuries and enhances the riding experience.
Training for Safe Water Crossings
Participating in riding courses is recommended to develop skills necessary for safe water navigation. Training should cover techniques for maintaining vehicle stability and effective control during water crossings. Understanding the behavior of different water depths and currents aids in making informed decisions.
Practical exercises in controlled environments can help riders gain confidence. Knowledge of specific vehicle limitations, whether an ATV or side by side, is integral to a rider’s training regimen.
Accident Prevention Strategies
To minimize accidents, riders are encouraged to assess water depth and check for unseen obstacles. Patience is key when evaluating the terrain and choosing the right path. Maintaining a moderate speed prevents loss of control.
Teams should employ hand signals and establish clear communication protocols when navigating in groups. Regular vehicle maintenance checks ensure all components function correctly, reducing the likelihood of mechanical failures during a crossing. Implementing these strategies greatly enhances safety and mitigates potential hazards.
Impact on Nature and Wildlife

Using ATVs and Side by Sides in water crossing can greatly impact the environment. Key concerns include effects on wildlife conservation, habitat restoration, water quality, and recreational opportunities.
Wildlife Conservation Efforts
Trails through natural habitats can disturb wildlife. Motorized vehicles, when crossing bodies of water, may disrupt the ecosystems of species like amphibians and fish. Conservation groups are striving to raise awareness and promote responsible usage of these vehicles.
Efforts include restrictions in sensitive areas and partnerships with local communities. The advantages of such actions lead to reduced stress on animals and ecosystems while promoting sustainable interactions between humans and wildlife.
Habitat Restoration and Water Quality
Water crossing activities can lead to soil erosion and sedimentation, which affect habitat quality. Efforts in habitat restoration often focus on repairing areas damaged by such activities, improving structural integrity.
Regulatory measures ensure vehicles maintain a safe distance from critical zones. Water quality initiatives aim to reduce pollutants from vehicle emissions, mitigating risks to aquatic life. Collaborative programs between environmental groups and off-road clubs support these restoration and protection processes.
Public Benefits and Recreational Impact
Public areas experience varied impacts from recreational activities such as hiking, hunting, and ORV sports. While these activities support local economies, ATVs and Side by Sides may increase erosion and decrease trail usability for other users.
Programs emphasize balancing recreational use with ecological protection. Educating operators on sustainable practices is key. The goal is to enhance public benefits while minimizing harm, ensuring safe, enjoyable environments for all.
Strategies for Sustained Usage

Balancing the needs of recreation with conservation is essential for long-term water crossing sustainability. Effective management strategies and understanding how timber harvests interact with water quantity are vital components.
Creating Effective Management Strategies
Effective management plans play a crucial role in maintaining sustainable water crossing methods. These plans should address factors such as environmental impact and usage levels. Stakeholder engagement ensures that the concerns of various groups, including recreational users and conservationists, are considered.
Implementation of monitoring programs can help track the impact of crossings over time and adjust strategies accordingly. Regulatory frameworks and enforcement are also key to maintaining the balance between usage and conservation, preventing degradation of these vital resources.
Balancing Recreational Use and Conservation
Recreational use and conservation must coexist to ensure water crossings remain viable for both enthusiasts and the environment. Managed access points and designated crossings can reduce ecological damage. Education and awareness programs can inform users of the best practices for minimizing environmental impact.
Encouraging responsible behavior and adhering to designated routes help protect sensitive areas. Additionally, partnerships with conservation groups can promote sustainability through joint efforts in habitat restoration and conservation initiatives.
Influences of Timber Harvest and Water Quantity
Timber harvest activities can significantly impact water quantity and quality, necessitating careful planning and management.
BMPs (Best Management Practices) assist in minimizing negative effects on adjacent water resources. Buffer zones and selective cutting can help protect waterways from sediment and pollution.
Balancing timber harvest with water resource management ensures a sustainable approach that supports environmental needs.
Understanding the relationship between forestry activities and water dynamics is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems. Collaboration among resource managers and stakeholders is essential for developing comprehensive management strategies.