As an Amazon Associate I may earn a commission from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
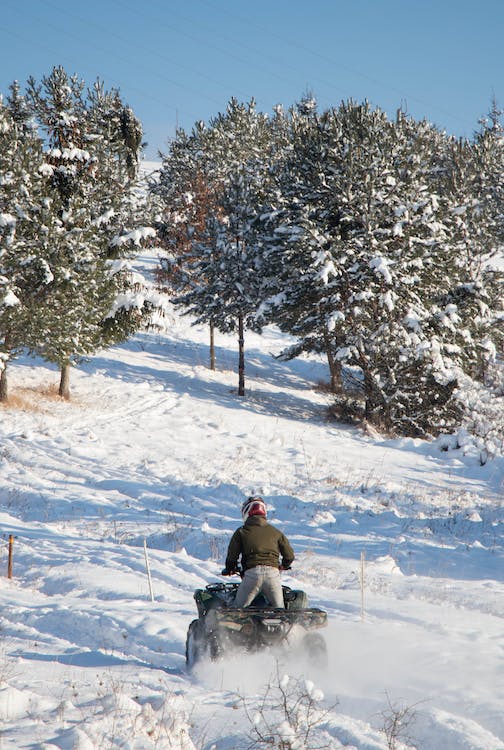
Off-road enthusiasts are familiar with the thrill of all-terrain vehicles (ATVs) and Side by Sides carving trails in the great outdoors. Yet, each comes with a differing environmental footprint that merits attention.
ATV trail preservation is crucial for minimizing erosion and maintaining natural habitats, whereas Side by Side footprint management focuses on reducing disturbances through innovative techniques.

Trail preservation for ATVs largely hinges on sustainable practices that mitigate the impact on plant life and soil integrity. These efforts are essential to ensure that trails remain usable and ecosystems continue to flourish.
On the other hand, Side by Sides, with their larger size, demand a focus on footprint management to prevent broader environmental disruptions.
Engagement with these vehicles requires a balance between enjoying off-road activities and safeguarding natural settings. By approaching ATV trail preservation and Side by Side footprint management with informed strategies, outdoor enthusiasts can contribute positively to the sustainability of the environments they explore.
Environmental Concerns and Impact Assessment

ATVs and Side by Sides affect ecosystems in various ways, including soil degradation, disturbance to wildlife, and pollution. Each vehicle type has a unique environmental footprint that impacts trail systems and forest preserves. Understanding these effects is crucial for effective wilderness management.
Defining Ecological Footprints of ATVs and Side by Sides
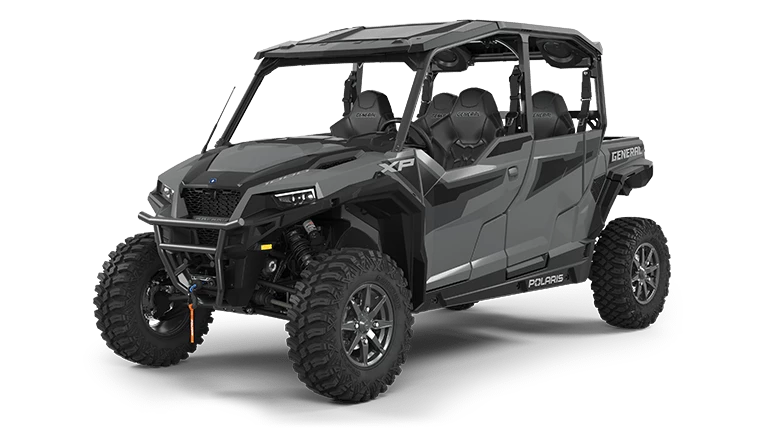
Both ATVs (All-Terrain Vehicles) and Side by Sides have distinctive ecological footprints. ATVs, typically lighter and smaller, often cause less physical disturbance compared to Side by Sides, which are bulkier and exert more pressure on the trail systems.
Impact varies based on vehicle design, trail usage, and user behavior. For instance, repeated trips can worsen trail erosion and widen paths, altering habitat conditions significantly.
Furthermore, ATVs might navigate narrower trails, reducing overall land impact. Yet, reckless use and lack of management can lead to extensive environmental degradation.
Assessing the footprint helps in implementing effective conservation strategies and designing trails that align with sustainable wilderness management practices.
Impact on Soil and Vegetation
ATVs and Side by Sides both contribute to soil compaction, leading to decreased soil porosity and increased runoff. This impacts water absorption and alters plant root systems, reducing vegetation growth.
Trail systems affected by these vehicles often experience accelerated erosion, changing the landscape and exposing soil to further damage.
Vegetative cover may be destroyed by consistent vehicle passages, especially if trail regulations are not enforced. Such habitat alterations affect biodiversity, as native plants struggle to thrive under increased human and mechanical pressure. The forest preserve areas are particularly sensitive, requiring careful monitoring to maintain ecological balance.
Wildlife Disturbance and Habitat Disruption
Wildlife habits and behaviors are often disrupted by noise, dust, and presence of ATVs and Side by Sides. Animals may vacate critical habitat areas, experiencing stress from these disturbances.
This becomes particularly concerning in sensitive regions like forest preserves, where biodiversity is a key conservation focus.
Migratory paths might be blocked or new paths formed, leading wildlife to areas ill-suited for their needs. Habitat disruption can also foster invasive species, outcompeting native populations.
Effective trail design and usage guidelines help mitigate these impacts, ensuring wildlife conservation remains a priority in wilderness management.
Water Quality and Erosion Effects
Soil erosion caused by ATVs and Side by Sides directly impacts nearby water bodies. Sedimentation can lead to reduced water quality, affecting aquatic habitats and potentially altering pH levels.
Moreover, contaminants from vehicles, such as oils and fuels, may pollute water sources, posing risks to aquatic life and human water supplies.
The design of trail systems near water bodies requires strategic planning to limit erosion. Forest preserve management focuses on minimizing run-off and protecting riparian zones to maintain healthy ecosystems. Efforts to repair and restore trails encourage sustainable use and conservation efforts.
Noise Pollution and Its Consequences
ATVs and Side by Sides generate significant noise levels, leading to both human and wildlife disturbances. Noise pollution can disrupt wildlife communication, mating behaviors, and cause stress among animals.
For trail users, excessive noise diminishes the serene experience of natural settings and may discourage organic trail usage.
Distance and buffer zones within trail systems can help reduce noise pollution. Moreover, adopting quieter vehicle technology and promoting user-guided regulation may further alleviate these concerns. Wilderness management strategies need to incorporate noise assessment measures to enhance the overall integrity of forest preserves.
Trail Preservation Strategies

Effective trail preservation balances recreational usage with environmental conservation. It integrates eco-friendly design, sustainable maintenance, and adaptive policies to maintain trail systems used in activities like hiking and riding.
Eco-friendly Trail Design and Construction
Designing trails with sustainability in mind is crucial. This involves assessing soil types, water flow, and vegetation to minimize environmental disruption.
Trails are often designed to follow natural contours of the land, reducing erosion. Materials such as gravel or mulch are used to stabilize paths.
Well-planned drainage systems help manage water flow, preventing trail degradation.
Additionally, narrow and single-track pathways are preferred to minimize ecological footprints. In areas with sensitive ecosystems, elevated boardwalks provide minimal impact solutions.
Sustainable Trail Maintenance Practices
Regular upkeep is essential to trail preservation. Routine inspections identify wear and tear early, allowing for timely repairs. Volunteers often engage in maintenance days to address trail erosion, clear debris, and manage vegetation overgrowth.
Use of non-invasive plant species around trails can enhance stabilization and restore native habitats. Techniques such as armoring using rocks or logs reinforce trail durability.
Dedicated maintenance plans consider seasonal weather patterns, ensuring year-round trail accessibility and safety.
Revisiting Recreational Riding Policies
Adaptive recreation management policies are necessary to accommodate both environmental and recreational needs. These policies may involve limiting trail access during wet conditions to prevent damage.
Designating trails for specific types of recreational activities, like hiking or off-road vehicle use, reduces conflicts and environmental strain. Education programs focusing on trail etiquette and environmental impacts encourage responsible usage. Implementing usage fees can also fund conservation efforts, balancing the enjoyment of trails with their longevity.
Comparative Analysis of ATV and Side by Side Usage
ATVs and Side by Sides are both popular choices for trail enthusiasts. They each have unique impacts on trails, distinct usage purposes, and different cost-benefit considerations. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about which vehicle best suits their needs and the environment.
Trail Impact by Vehicle Type
ATVs, being more compact, exert less pressure per square inch on trails compared to larger Side by Sides. Their smaller size allows easier navigation through narrow paths, reducing the need for trail widening.
In contrast, Side by Sides are heavier and often require more extensive trails. This can lead to more soil displacement and vegetation damage. However, their wider tires distribute weight more evenly, potentially lessening erosion on well-maintained paths.
Popularity and Purpose of Use
ATVs are often chosen for solo adventures and competitive racing due to their agility and speed. They’re a favorite among thrill-seekers who prefer tight landscapes and quick maneuvers. Their versatility in rugged terrains makes them ideal for exploring remote areas.
Side by Sides, accommodating more passengers, are frequently used for group outings and family expeditions. Their design allows for leisurely rides with friends and family, and they are often employed for work purposes such as hauling equipment in less accessible locations.
Cost-Benefit Assessment of Vehicle Types
ATVs typically have a lower initial purchase price and cost less to maintain. They provide a cost-effective option for those seeking affordable and solo recreational riding experiences. Fuel efficiency is generally higher than that of Side by Sides.
Side by Sides, though more expensive initially, offer increased functionality and capacity. They provide a higher payload and passenger capacity, making them a sound investment for those needing a versatile vehicle for both leisure and utilitarian purposes. The ability to carry more gear and people can offset the higher costs over time.
Regulatory Framework for Off-road Vehicles

Regulations governing off-road vehicles are crucial for maintaining ecological balance. These frameworks encompass state and federal laws, the roles of organizations like the Adirondack Park Agency, and the enforcement protocols that ensure compliance.
State and Federal Laws
State and federal laws regulate the use of off-road vehicles to minimize environmental impact. State regulations differ significantly, often influenced by local ecosystems and conservation needs. For instance, some states might require permits for off-road vehicles to operate on public lands.
Federal laws are generally less variable, focusing on overarching guidelines that protect national parks and wildlife areas. They often include restrictions on emissions, noise, and prohibited areas. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a role in enforcing these guidelines through various initiatives aimed at preserving natural resources.
Role of the Adirondack Park Agency
The Adirondack Park Agency holds a pivotal role in managing off-road vehicle use within park boundaries. They develop strategies that balance recreation with conservation. Management plans are crafted to ensure sustainable use of trails and natural areas.
Collaborating closely with the DEC, the Agency sets stringent criteria for trail development and usage. These criteria aim to protect the park’s unique biodiversity. Through educational programs, they also promote responsible vehicle use among visitors. This proactive approach helps to mitigate potential environmental damage while promoting recreational activities.
Enforcement Mechanisms and Penalties
Enforcement strategies are critical in ensuring adherence to regulations. Law enforcement agencies collaborate with environmental bodies like the DEC to monitor compliance. This involves regular inspections and checkpoints on popular trails to discourage illegal activity.
Penalties for non-compliance can be severe, including fines or revocation of permits. Repeat offenders might face more stringent actions, such as confiscation of vehicles.
Educational initiatives also serve as a preventive measure, emphasizing the significance of protecting natural habitats.
Engagement with community stakeholders is fostered to enhance compliance and ensure these penalties are effectively communicated. By doing so, the regulatory framework aims to promote a culture of responsibility and sustainability among off-road vehicle users.
ATV and Side by Side Market Dynamics

The market for ATVs and Side by Sides is characterized by growth trends and significant economic influence on environmental conservation efforts.
Predictions for the industry’s expansion provide insight into market behaviors and potential trails for both recreational and conservation-focused activities.
Current Market Overview and Trends
Since 2023, the ATV and Side by Side market has displayed notable growth, with a market size close to impressive figures.
The demand for these outdoor vehicles is driven by the rising popularity of recreational activities and outdoor sports.
The CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) is predicted to maintain a steady upward trajectory, a testament to the expanding consumer base.
Technology advancements in vehicle design also contribute to the diversity and appeal of available models.
Economic Influence on Trail Preservation Efforts
The economic impact of the ATV and Side by Side market significantly affects trail preservation funding.
Revenue from sales and associated recreational activities feeds directly into environmental and trail maintenance budgets.
This financial support ensures sustainability in trail infrastructure and aids in addressing vehicle footprint concerns.
Stakeholders see economic growth as a key element in financing ecological preservation, promoting a balance between market expansion and environmental responsibility.
Forecast Period and Growth Predictions
Looking ahead to the forecast period of 2025-2029, analysts expect continued market growth.
Projections indicate an increase in market size, potentially reaching remarkable figures by 2029.
This expansion is attributable to enhanced vehicle features that appeal to a broad consumer segment.
The predicted growth supports ongoing research and development efforts, which may further mitigate environmental impacts while maintaining consumer interest and satisfaction.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Examining trail preservation and footprint management reveals a dynamic interplay between successful conservation and community involvement.
Highlighted are real-world examples, innovative conservation programs, and the critical role of community engagement in trail management.
Examples of Successful Trail Preservation
In recent years, several trail systems have modeled excellent practices in preserving natural environments while accommodating off-road vehicle use.
The Appalachian Trail, renowned for its conservation strategies, demonstrates how limited vehicle access and designated routes can preserve the landscape.
In Utah, sustainable trail design focuses on drainage systems and erosion control. Such measures prevent soil degradation and maintain the trail’s integrity.
Another notable case is Colorado’s use of volunteer conservation groups to routinely assess trail conditions and implement repairs promptly.
ATV and Side by Side Conservation Programs
Programs dedicated to ATV and Side by Side use have emerged, promoting sustainable practices.
The Tread Lightly! initiative emphasizes responsible recreation to minimize ecological footprints. They provide guidelines on trail usage that include avoiding wet conditions and staying on marked paths.
Furthermore, California’s Off-Highway Vehicle program funds maintenance and restoration projects.
Such programs balance recreational access with environmental protection, ensuring long-term usability of trails. They focus on research-based strategies to reduce impact, providing educational resources to recreational users.
Community Involvement in Trail Management
Community engagement plays an integral role in trail management and conservation.
Volunteer groups often collaborate with local governments to maintain and protect trial systems.
Organizations like “Friends of the Appalachian Trail” illustrate how community-driven efforts can lead to significant improvements in sustainability.
Workshops and cleanup events foster a strong sense of stewardship among local residents, encouraging active participation in conservation efforts.
By involving the community, these initiatives build awareness and support for preserving natural landscapes, demonstrating how local involvement ensures the longevity of recreational trails.
Future of Off-road Vehicle Recreation
Advancements in technology, evolving tourism patterns, and economic considerations are shaping the future landscape of off-road recreation.
Significant focus is on enhancing trail experiences and preserving natural environments.
Technological Innovations and GPS Navigation
The integration of technological advancements is revolutionizing off-road vehicle navigation.
Real-time GPS systems provide precise location tracking, helping adventurers safely explore diverse landscapes.
This technology not only offers enhanced safety but also optimizes route planning by identifying sustainable trails, minimizing environmental impact.
The development of apps tailored for off-road enthusiasts continues to rise, offering interactive trail maps and weather updates, fostering a balance between exploration and preservation.
Impact of Tourism and Economic Development
Off-road recreation plays a crucial role in tourism and contributes to local economic development.
Regions with well-maintained trails attract enthusiasts, boosting local businesses such as hotels, equipment rentals, and dining establishments.
This tourism influx promotes job creation and fosters community growth.
Managing this growth responsibly ensures economic benefits while protecting the ecological integrity of natural habitats and maintaining the quality of life for residents.
Challenges and Opportunities for Trail Preservation
Trail preservation faces challenges such as erosion, habitat disruption, and litter. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovative solutions.
Collaborative efforts among stakeholders can lead to sustainable trail design and maintenance strategies.
Educating riders about the environmental impact of their activities encourages responsible recreation.
Financial support for preservation efforts ensures the longevity of trails, balancing environmental protection with recreational interests.